Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2005; 11(18): 2822-2826
Published online May 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i18.2822
Published online May 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i18.2822
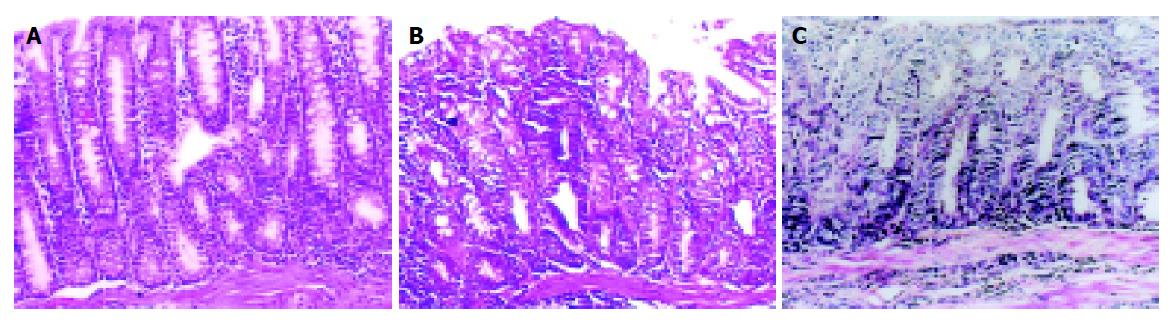
Figure 1 Grade of the tissue lesions under microscopic examination.
A: mild dysplasia (×100); B: moderate dysplasia (×100); C: severe dysplasia in model group (×200).
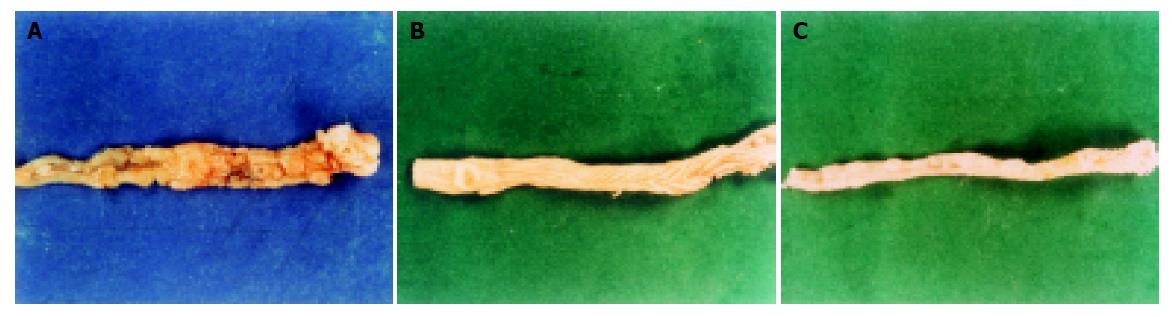
Figure 2 Macroscopic examination.
A: Model-agent group (32nd wk). Multiple nodes of tumors located in the large intestinal mucosa with the intestinal wall becoming thicker and rigid; B: Sulindac-preventative group (32nd wk). Only two nodes of tumors of diameter about 2 mm are located at the large intestinal mucosa; C: Curative group (32nd wk). Several nodes of tumor are located in the large intestinal mucosa with disappeared plica.
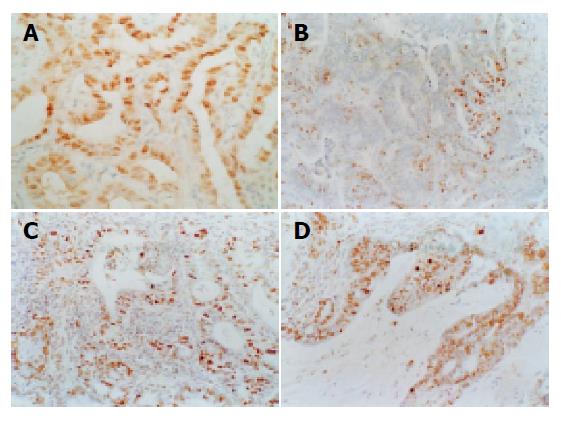
Figure 3 The distribution of proliferation and apoptotic cells.
A: Model-agent group: there are a large number of positive cells with PCNA staining in large intestinal cancer and evenly distributed, ×200; B: Model-agent group: there are a small number of apoptotic cells in the large intestinal cancer. TUNEL, ×200; C: Curative group: there are a large number of apoptotic cells in the large intestinal cancer. TUNEL, ×200; D: Preventative group: there are a large number of apoptotic cells in the large intestinal cancer. TUNEL, ×200.
- Citation: Sun BC, Zhao XL, Zhang SW, Liu YX, Wang L, Wang X. Sulindac induces apoptosis and protects against colon carcinoma in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(18): 2822-2826
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i18/2822.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i18.2822