Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2005; 11(18): 2714-2719
Published online May 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i18.2714
Published online May 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i18.2714
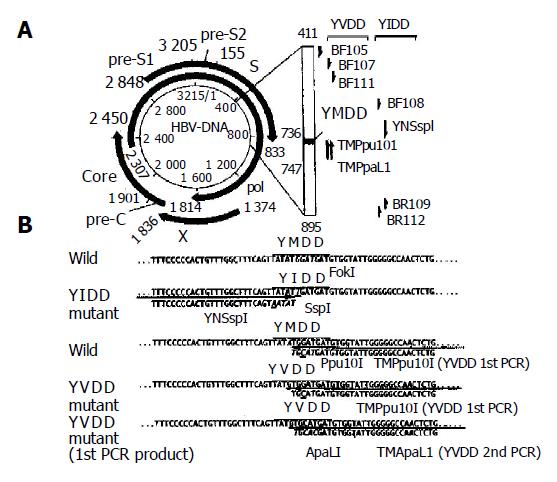
Figure 1 Schematic representation of analyzed partial DNA polymerase gene and primers used to detect two YMDD mutants (A) and nucleotide sequences of DNA polymerase gene including YMDD motif and primers for specific detection of both YIDD and YVDD mutants (B).
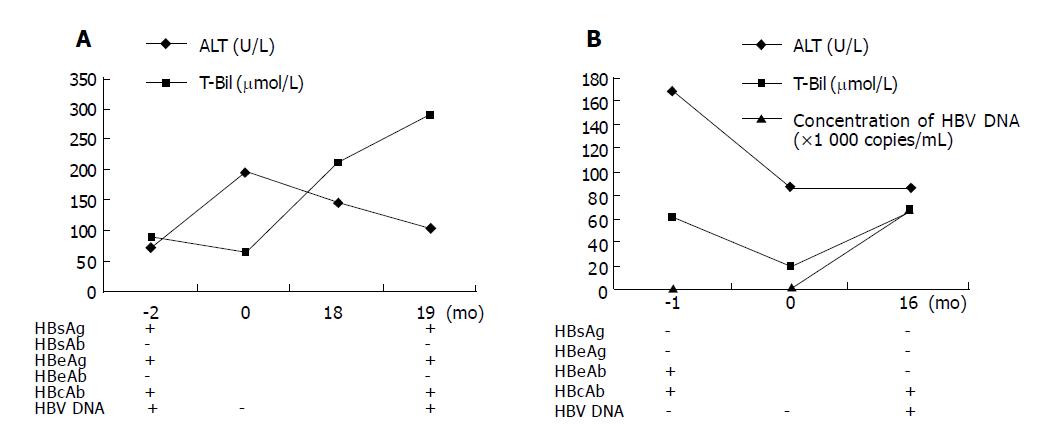
Figure 2 Clinicopathological data of patient 1 (A) and patient 2 (B) before and after OLT.
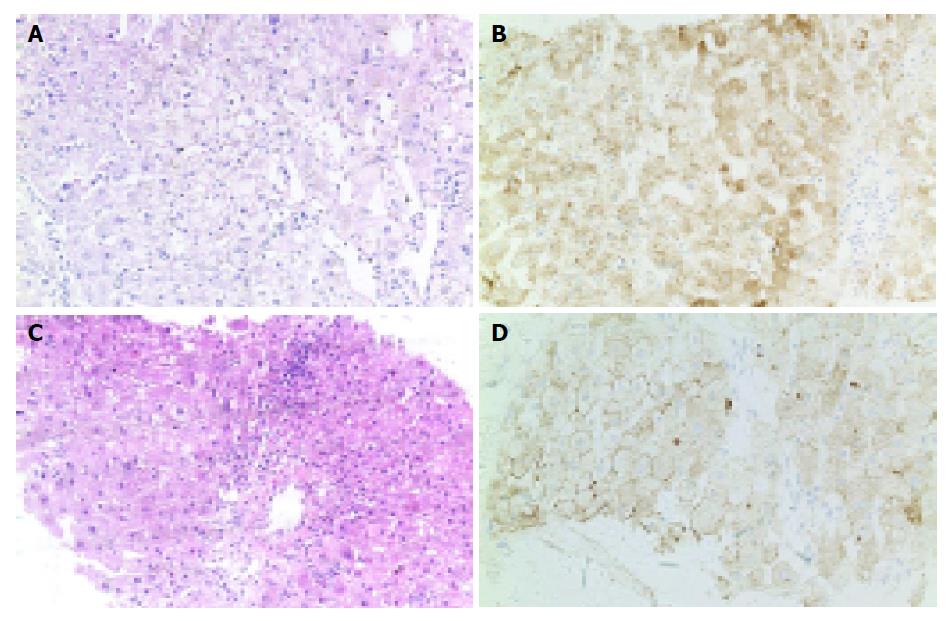
Figure 3 Liver biopsy of patients 1 (A and B) and 2 (C and D) 19 and 16 mo after OLT.
A and C: HE, ×20; B and D: positive immunohistochemical staining for HBsAg in hepatocytes (IHC, ×20).
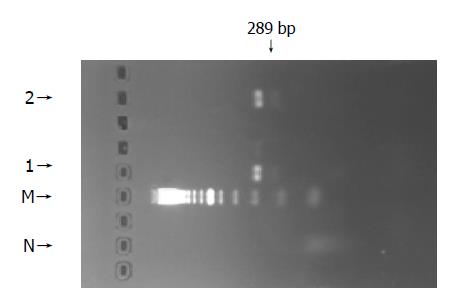
Figure 4 PCR-amplified products of a 289-bp fragment of DNA polymerase gene of HBV including YMDD motif in patients 1 and 2.
N: normal; M: DNA marker; 1: patient 1; 2: patient 2.
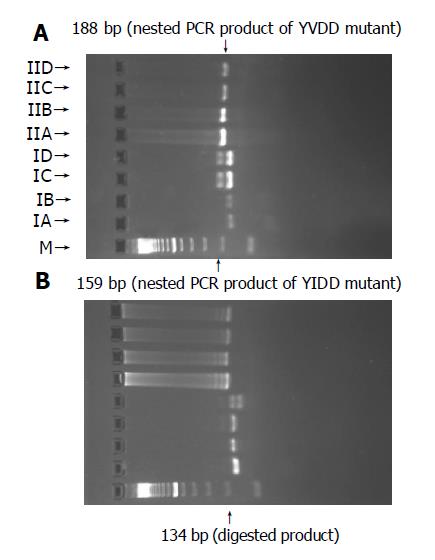
Figure 5 PCR-RFLP analysis pattern of patient 1 (A) and patient 2 (B).
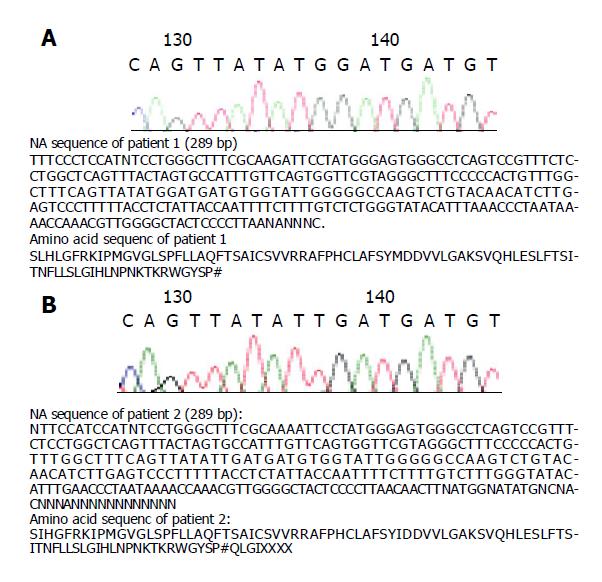
Figure 6 DNA sequence of patient 1 (A) and patient 2 (B).
- Citation: Pei F, Ning JY, You JF, Yang JP, Zheng J. YMDD variants of HBV DNA polymerase gene: Rapid detection and clinicopathological analysis with long-term lamivudine therapy after liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(18): 2714-2719
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i18/2714.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i18.2714