Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 15, 2004; 10(8): 1093-1097
Published online Apr 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i8.1093
Published online Apr 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i8.1093
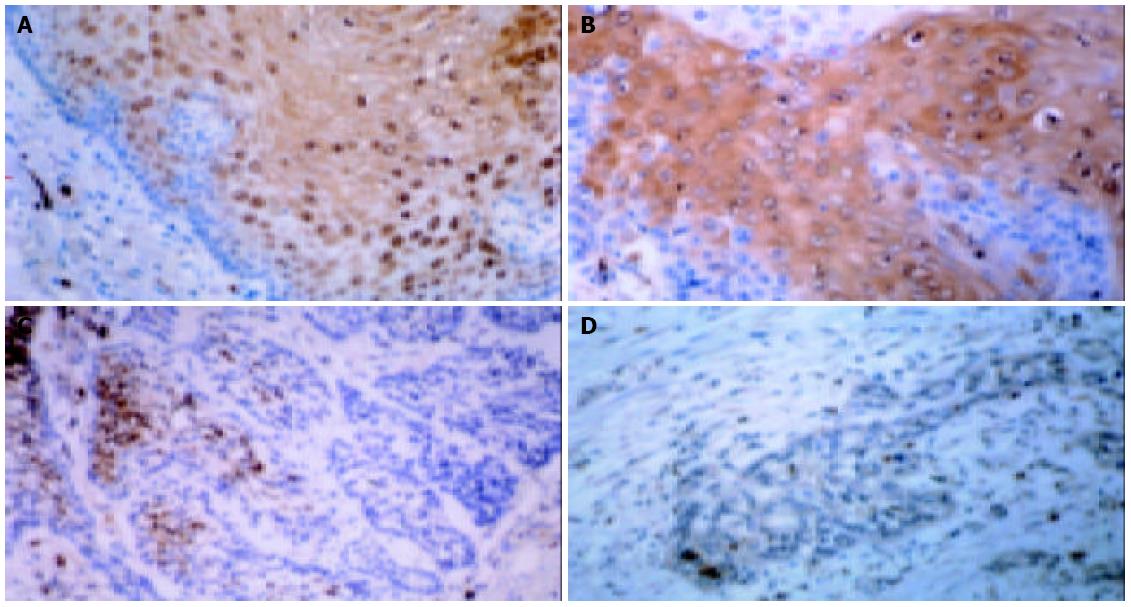
Figure 1 Immunohistochemistry for MRP8 in esophageal carcinoma tissues and normal epithelia (original magnification: × 400).
A: MRP8 expression in suprabasal layers of normal esophageal epithelium; B: MRP8 staining in well differentiated carcinoma; C: MRP8 staining in moderately differentiated carcinoma; D: MRP8 staining in poorly differentiated carcinoma.
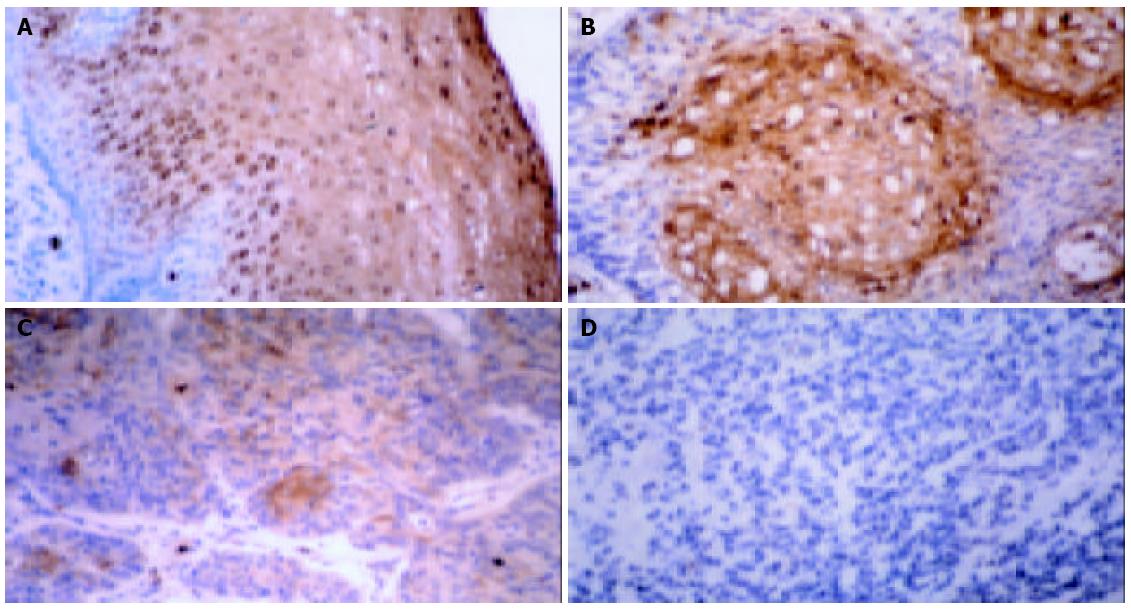
Figure 2 Immunohistochemistry of MRP14 in normal esophageal epithelium (A) and well (B), moderately (C) and poorly differ-entiated (D) carcinoma tissues.
Normal esophageal epithelium showed strongly positive staining for MRP14. However, its staining in poorly differentiated carcinoma was significantly weaker than that in well and moderately differentiated carcinomas. Granulo-cytes and monocytes were also positively stained in all the sections. Original magnification: × 400.
- Citation: Kong JP, Ding F, Zhou CN, Wang XQ, Miao XP, Wu M, Liu ZH. Loss of myeloid-related proteins 8 and myeloid-related proteins 14 expression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma correlates with poor differentiation. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(8): 1093-1097
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i8/1093.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i8.1093