Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 1, 2004; 10(7): 1019-1027
Published online Apr 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i7.1019
Published online Apr 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i7.1019
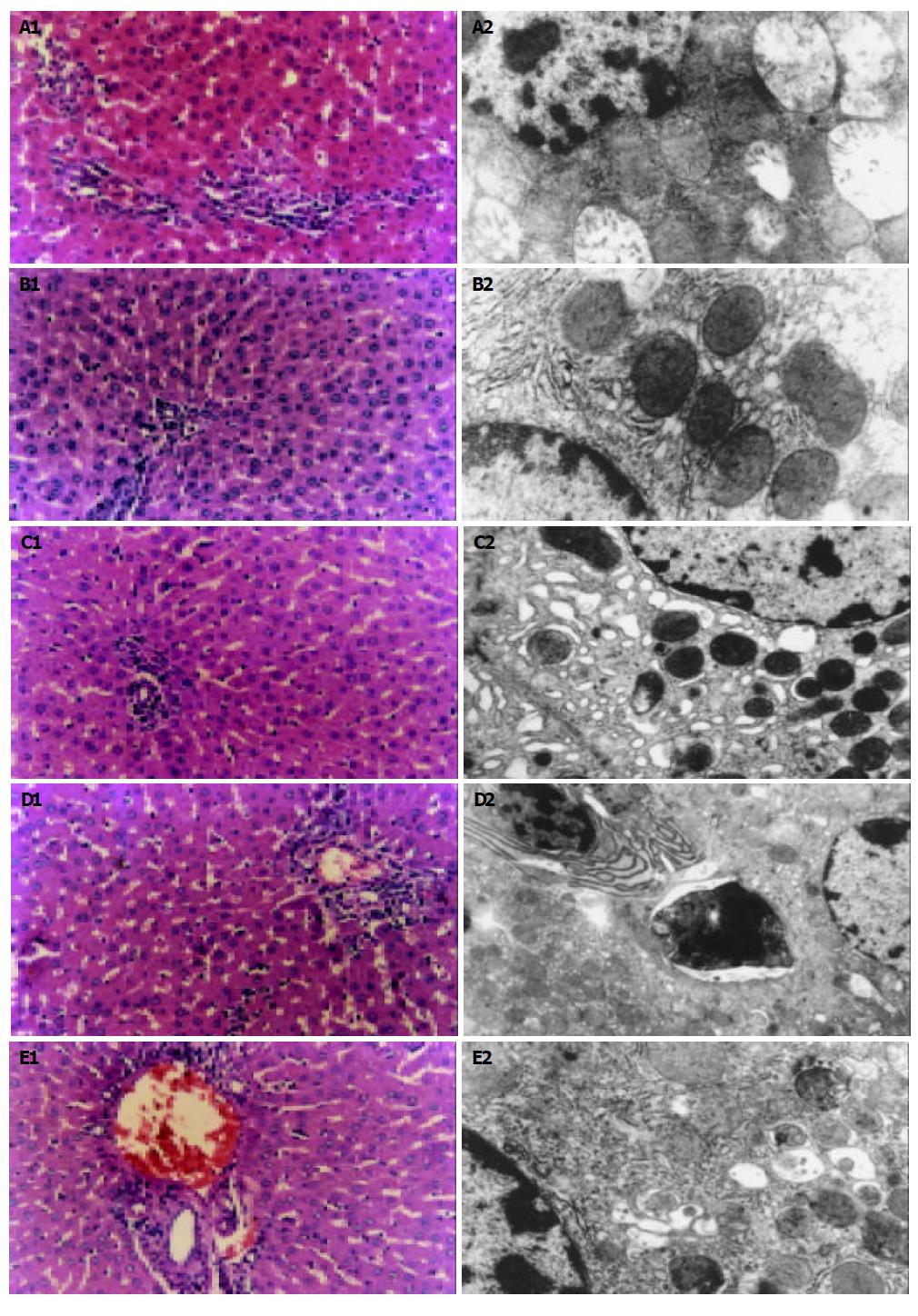
Figure 1 Changes of cellular structure and ultrastructure after treatment with IR, IP, IR + PMA, IP + CHE, and IP + PD98059.
A1-2: Effect of ischemia and reperfusion on hepatocytes, B1-2: Cytoprotective effects of ischemia preconditioning, C1-2: Effects of ischemia preconditioning after stimulation of PKC with PMA, D1-2: Proteetive effect of ischemia preconditioning abolished by inhibition of PKC with chelerythrine, E1-2: Cytoprotective effect of ischemia preconditioning reverted by PD98059
Figure 2 Changes of cellular ultrastructure after treatment with IR, IP, IR + PMA, IP + CHE, and IP + PD98059.
A: Effect of hy-poxia reoxygenation on hepatocytes, B: Cytoprotective effects of hypoxic preconditioning, C: Preconditioning effects mim-icked by stimulation of PKC with PMA, D: Preconditioning protection abolished by inhibition of PKC with chelerythrine, E: Cytoprotection of preconditioning reverted by PD98059.
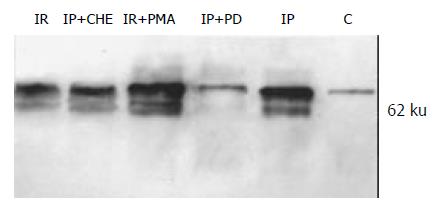
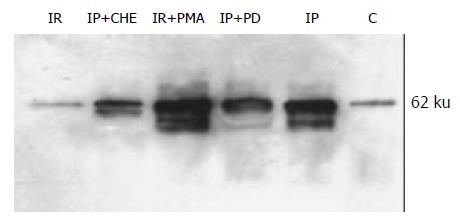
Figure 3 Expression of P44 and P42 MAPKs in rat liver.
Figure 4 Expression of P44 and P42 MAPKs in isolated human hepatocytes.
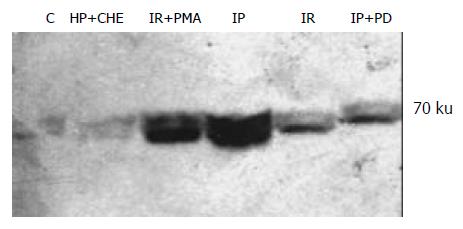
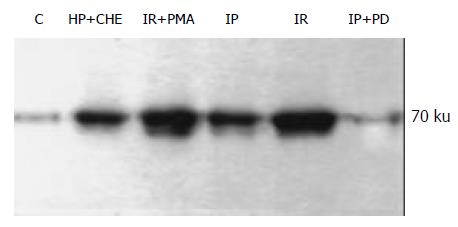
Figure 5 Expression of HSP70 in rat liver
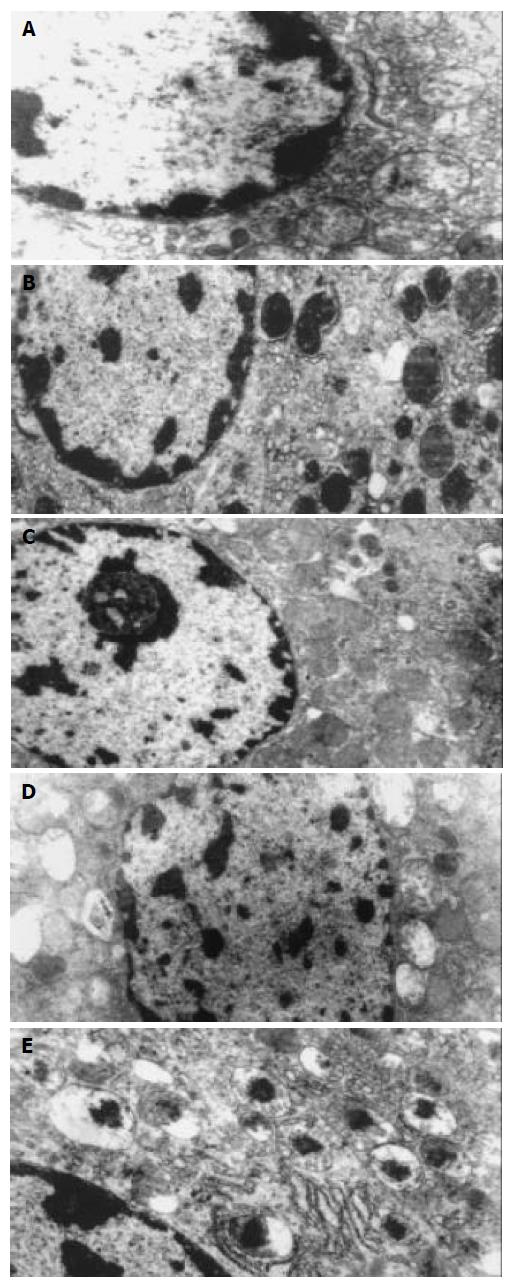
Figure 6 Changes of cellular ultrastructure after treatment with IR, IP, IR+PMA, IP+CHE, and IP+PD98059.
A: Effect of hypoxia reoxygenation on hepatocytes, B: Cytoprotective effects of hypoxic preconditioning, C: Preconditioning effects mimicked by stimulation of PKC with PMA, D: Preconditioning protection abolished by inhibition of PKC with chelerythrine, E: Cytoprotection of preconditioning reverted by PD98059.
- Citation: Gao Y, Shan YQ, Pan MX, Wang Y, Tang LJ, Li H, Zhang Z. Protein kinase C-dependent activation of P44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase and heat shock protein 70 in signal transduction during hepatocyte ischemic preconditioning. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(7): 1019-1027
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i7/1019.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i7.1019