Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 15, 2004; 10(20): 2989-2993
Published online Oct 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.2989
Published online Oct 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.2989
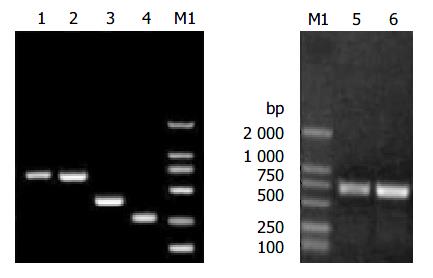
Figure 1 Electrophoresis of the fragments of HBV S gene.
Lane 1: HB fragment of complete HBV S gene; Lane 2: HB-SD fragment with the second-loop deletion of the α determinant; Lane 3: DNA fragment of HBV S gene from codon 1 to codon 138; Lane 4: DNA fragment of HBV S gene from codon 146 to codon 226; Lane 5: HBY fragments; Lane 6: HB-SDY fragments; Lane M1: DNA marker.
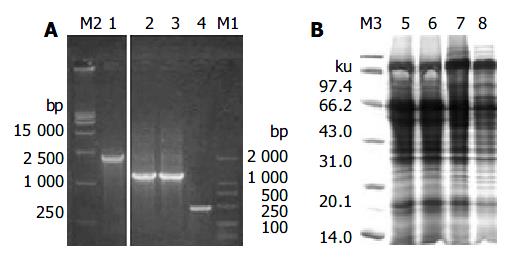
Figure 2 RFLP analysis of recombinant vectors of pHB-SD and pHB-SDY.
Lane M1: DNA marker; Lane 1: HB-SD fragment; Lane 2: pHB-SD candidate digested by restriction endonu-clease Hind III and Eco RI; Lane 3: pHB-SD candidate digested by restriction endonuclease Bam HI; Lane 4: pcDNA3 digested by restriction endonuclease Bam HI; Lane 5: pHB-SDY candi-date digested by restriction endonuclease Not I and Eco RI; Lane M2: DNA marker.
Figure 3 Screening integrants and SDS-PAGE analysis.
A: Screening integrants using PCR with AOX1 primers. Lane M2: DNA marker; Lane 1: PCR products of Mut+ transformant without gene of interest; Lane 2: PCR products of Muts transformants with pHBY; Lane 3: PCR products of Muts transformants with pHB-SDY; Lane 4: PCR products of pPIC9 alone. Lane M1 were DNA markers. B: Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE analysis of the recombinant proteins of pHB-SDY and pHBY. Lane M3: protein marker; Lane 5: cell lysate super-natants of yeast alone; Lane 6: yeast transformed with pPIC9; Lane 7: yeast transformed with pHBY; Lane 8: yeast trans-formed with pHB-SDY.
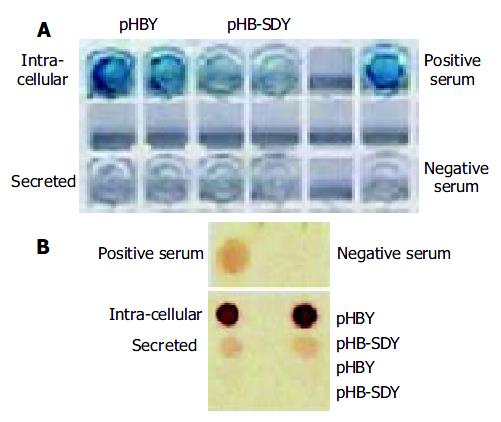
Figure 4 Antigenicity analysis of recombinant proteins using ELISA and immune dot blotting assay.
(A) ELISA, (B) immune dot blotting assay.
- Citation: Hu H, Peng XM, Huang YS, Gu L, Xie QF, Gao ZL. Yeast expression and DNA immunization of hepatitis B virus S gene with second-loop deletion of α determinant region. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(20): 2989-2993
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i20/2989.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.2989