Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 15, 2004; 10(20): 2944-2948
Published online Oct 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.2944
Published online Oct 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.2944
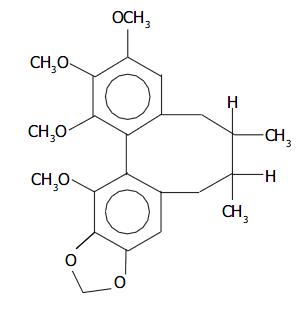
Figure 1 Chemical structure of Schisandrin B.
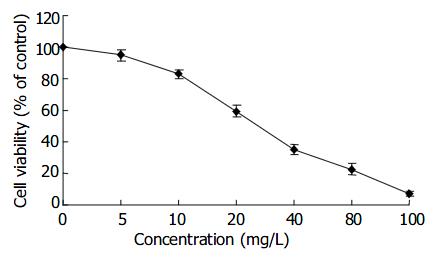
Figure 2 Inhibition rate of Sch B on proliferation of SMMC-7721 cells.
Cells were incubated at concentrations of Sch B for 48 h.
Figure 3 Cytocidal effect of Sch B on growth of human endot-helial ECV-304 cells, human hepatic HL-7702 cells, primary human fibroblast cells and human lymphocyte cells.
Cells were incubated at concentrations (10, 20, 40, 80, 160 mg/L) of Sch B for 48 h.
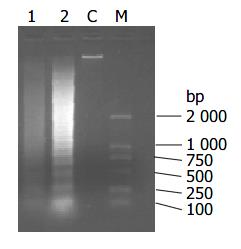
Figure 4 DNA fragmentation in SMMC-7721 cells treated with Sch B for 12 h.
M: size marker; C: control culture; lane 1: 20 mg/L Sch B treatment; lane 2: 40 mg/L Sch B treatment.
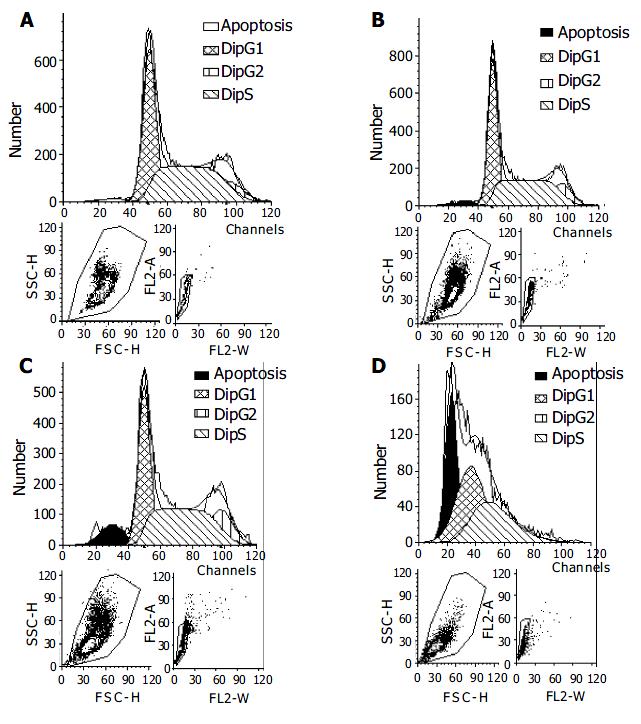
Figure 5 Cell apoptosis determined by flow cytometry.
SMMC-7721 cells were treated with Sch B at various concentrations (0, 10, 20, 40 mg/L, respectively A to D) for 48 h.
Figure 6 Effect of Sch B on expression of Hsp70, Caspases-3, - 7, -9 proteins.
SMMC-7721 cells were treated with Sch B for 48 h. After treatment, cell lysates were extracted, and the level of Hsp70, Caspases-3, -7, -9 proteins were analyzed by Western bolt analysis. Beta-actin was used as an internal loading control. Lane 1: control; Lane 2: 20 mg/L Sch B treatment; lane 3: 40 mg/L Sch B treatment.
- Citation: Wu YF, Cao MF, Gao YP, Chen F, Wang T, Zumbika EP, Qian KX. Down-modulation of heat shock protein 70 and up-modulation of Caspase-3 during schisandrin B-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(20): 2944-2948
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i20/2944.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.2944