Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 1, 2004; 10(19): 2870-2873
Published online Oct 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i19.2870
Published online Oct 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i19.2870
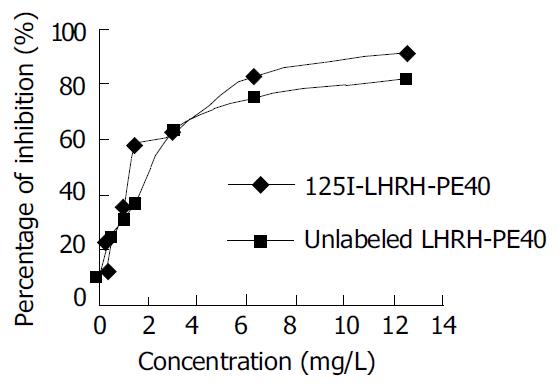
Figure 1 Inhibitory rates of unlabeled LHRH and 125I–LHRH on human liver cancer HEPG cell proliferation.
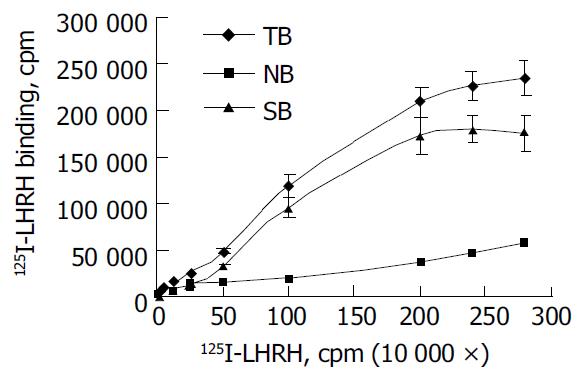
Figure 2 Saturation curve of 125I-LHRH binding to LHRHR of human liver cancer HEPG cells.
TB: total binding, NB: non-specific binding, SB: specific binding.
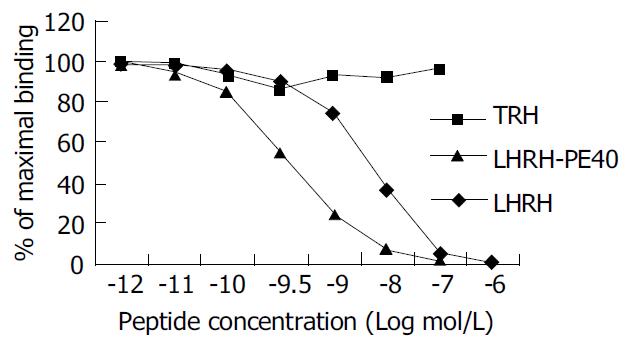
Figure 3 Inhibiting curve of competitive binding of non-labeled LHRH-PE40, LHRH and TRH to human liver cancer HEPG cell LHRHR with 125I-LHRH.
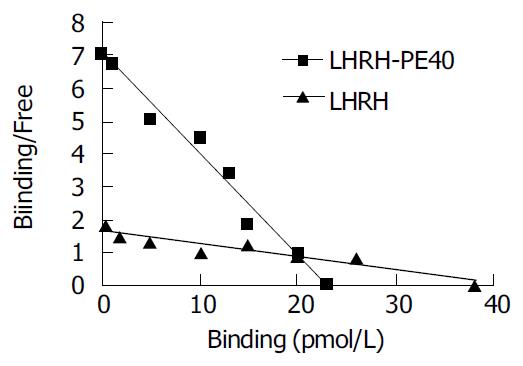
Figure 4 Scatchard analysis of LHRH-PE40 and LHRH bind-ing to LHRHR of human liver cancer HEPG cells.
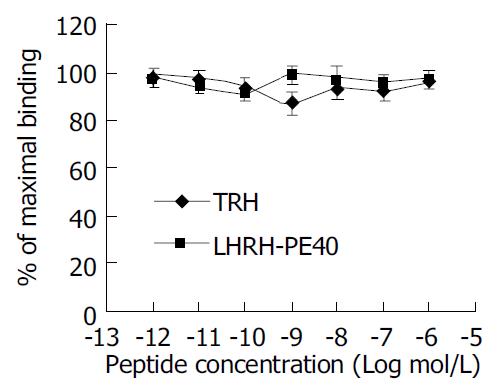
Figure 5 Inhibiting curve of competitive binding of non-labeled LHRH-PE40 and TRH to normal human liver cell LHRHR with 125I-LHRH.
-
Citation: Gong SL, Zhao G, Zhao HG, Lü WT, Liu GW, Zhu P. Ability of luteinizing hormone releasing hormone-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin 40 binding to LHRH receptor on human liver cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(19): 2870-2873 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i19/2870.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i19.2870