Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 1, 2004; 10(19): 2809-2813
Published online Oct 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i19.2809
Published online Oct 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i19.2809
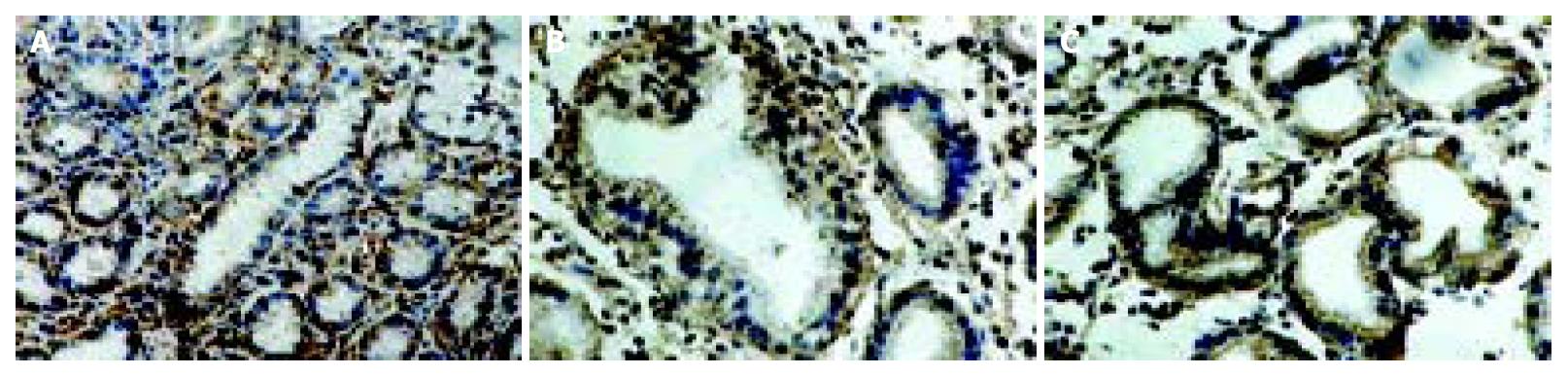
Figure 1 Immunostaining of cyclooxygenase-1 in the gastric mucosa with CSG (A), dysplasia (B) and gastric cancer (C) as shown by immunostaining.
In the gastric biopsies of cases of CSG, GA, IM and dysplasia, COX-1 immunostaining was detected in the foveolar and glandular epithelium including parietal cells, and in the subepithelial mononuclear inflammatory cells. Spotty cytoplasmic staining for COX-1 was seen in the gastric cancer cells.
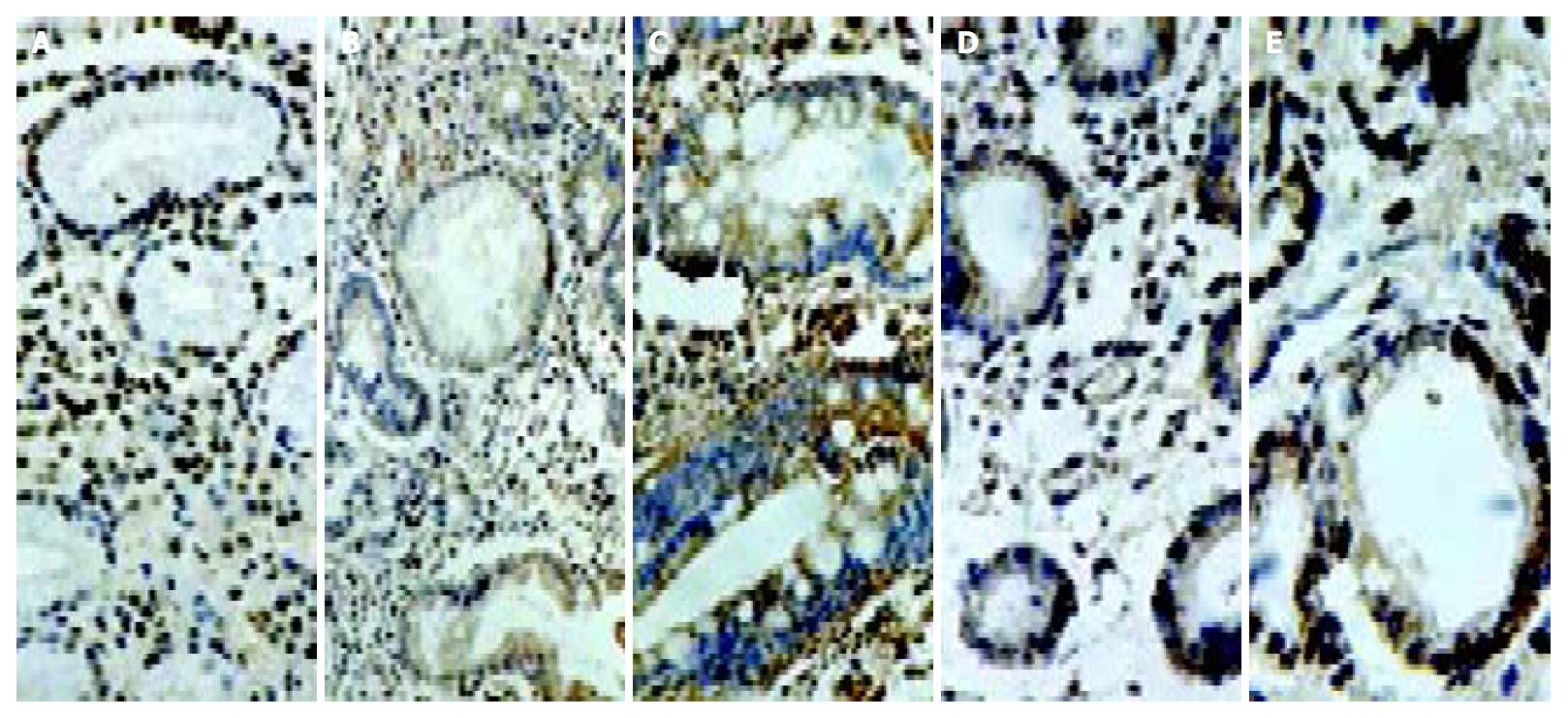
Figure 2 Immunostaining of cyclooxygenase-2 in the gastric mucosa with CSG (A), GA (B), IM (C), dysplasia (D) and gastric cancer (E).
CSG showing strong expression in foveolar and glandular epithelium and weak expression in mononuclear inflam-matory cells, myofibroblasts, and endothelial cells in the lamina propria; GA showing strong expression in the atrophic glands of the gastric mucosa; IM showing strong expression in intestinal epithelium and goblet cells; and gastric cancer showing strong expression in cancer cells.
-
Citation: Sun WH, Yu Q, Shen H, Ou XL, Cao DZ, Yu T, Qian C, Zhu F, Sun YL, Fu XL, Su H. Roles of
Helicobacter pylori infection and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in gastric carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(19): 2809-2813 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i19/2809.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i19.2809