Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 1, 2004; 10(1): 91-95
Published online Jan 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i1.91
Published online Jan 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i1.91
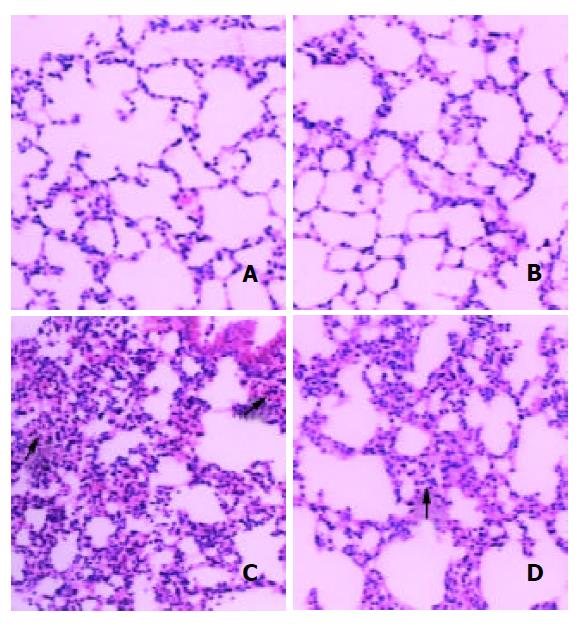
Figure 1 Typical HE staining.
The bar is 100 μm. A, B: the lungs from control of MT-/-and MT+/+ mice; C, D: the lungs from 750 mg/kg DMAA group of MT-/-and MT+/+ mice. Arrows in-dicate atelectasis and hemorrhage.
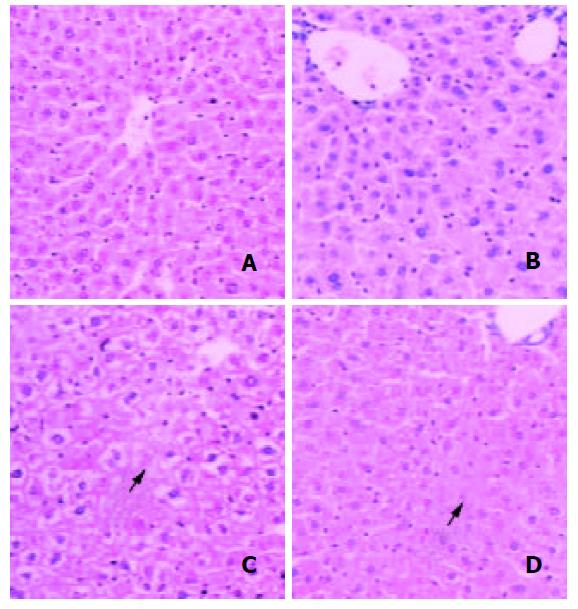
Figure 2 Typical HE staining.
The bar is 100 μm. A, B: the livers from control of MT-/-and MT+/+ mice; C, D: the livers from 750 mg/kg DMAA group of MT-/-and MT+/+ mice. The arrows indicate necrosis.
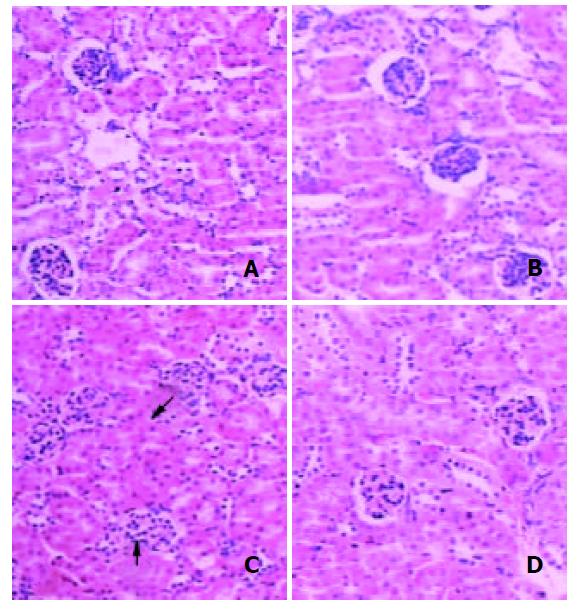
Figure 3 Typical HE staining.
The bar is 100 μm. A, B: the kidneys from control of MT-/-and MT+/+ mice; C, D: the kid-neys from 750 mg/kg DMAA group of MT-/-and MT+/+ mice. The arrows indicate the swelling of glomerulus and the surrounding tubular tissue and urinary space compression.
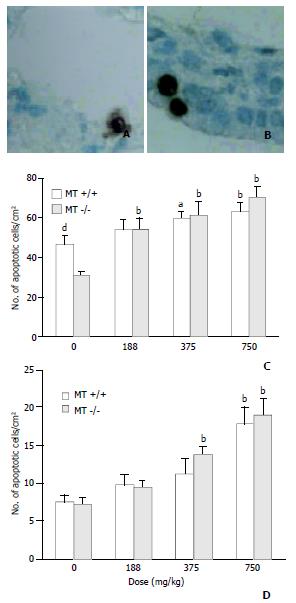
Figure 4 Apoptosis in lungs of MT+/+ and MT-/- mice detected by TUNEL twenty-four hours after oral DMAA treatment.
A: Typical apoptotic cells in alveolar area of MT-/- mice at a dose of 188 mg/kg body weight. Brown staining indicates the apoptotic cells. The bar is 20 μm. B: Typical apoptotic cells in bronchial area of MT-/- mice at a dose of 188 mg/kg body weight. Brown staining indicates apoptotic cells. The bar is 20 μm. C: AI in alveolar area. D: AI in bronchial area. All the values were expressed as -χ±s. ANOVA with subsequent post hoc’s test was performed for comparison of AI. a,bSignificant difference at P < 0.05, P < 0.01 when compared with the corresponding control group. c,dSignificant difference at P < 0.05, P < 0.01 when com-pared with the dose-matched MT-/- mice group.
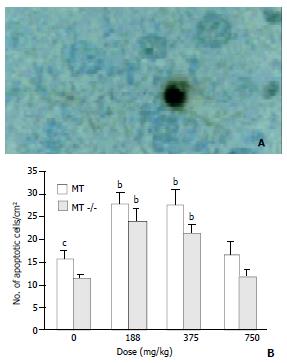
Figure 5 Apoptosis in livers of MT+/+ and MT-/- mice detected by TUNEL twenty-four hours after oral DMAA treatment.
A: Typical apoptotic cells in the liver of MT-/- mice at a dose of 188 mg/kg body weight. Brown staining indicates apoptotic cells. The bar is 20 μm. B. AI in the livers. All values were ex-pressed as -χ±s. ANOVA with subsequent post hoc’s test was performed for comparison of AI. a, bSignificant difference at P < 0.05, P < 0.01 when compared with the corresponding control group. c,dSignificant difference at P < 0.05, P < 0.01 when com-pared with the dose-matched MT-/- mice group.
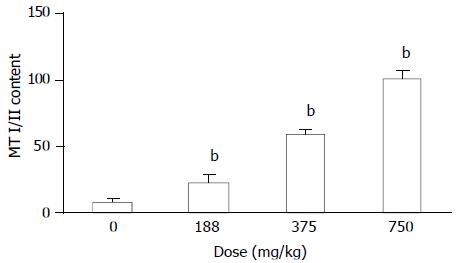
Figure 6 MT concentration in livers of MT+/+ mice detected by radio-immunoassay.
All the values were expressed as -χ±s. ANOVA with subsequent post hoc’s test was performed for comparison of AI. bSignificant difference at P < 0.01 when com-pared with the corresponding control group.
- Citation: Jia G, Gu YQ, Chen KT, Lu YY, Yan L, Wang JL, Su YP, Wu JCG. Protective role of metallothionein (I/II) against pathological damage and apoptosis induced by dimethylarsinic acid. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(1): 91-95
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i1/91.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i1.91