Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2021; 9(7): 1682-1695
Published online Mar 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1682
Published online Mar 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1682
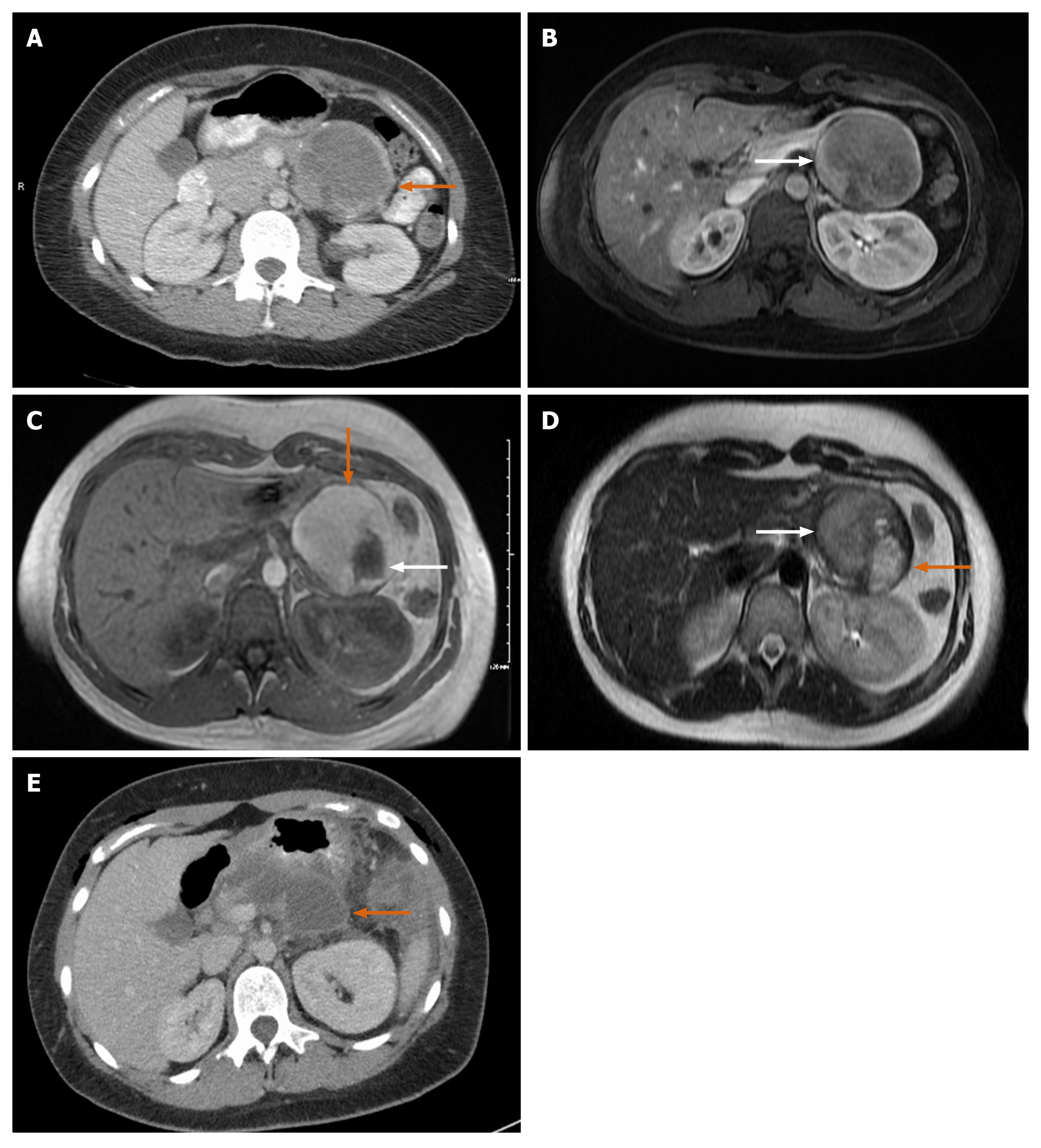
Figure 4 Magnetic resonance imaging.
A: Large mass with rim of calcification; B: Axial T1 image. White arrow: Solid enhancing component of the tumor; C: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T1 post gadolinium image, orange arrow: Large mass with bright T1 hyperintense signal; white arrow: Changes inside mass appear as hypointense; D: Axial T2 MRI white arrow: Heterogenous T2 signal in conjunction with the bright T1 signal (orange arrow in image C) is consistent with internal hemorrhage; orange arrow: T2 hyperintense in conjunction with hypointense appearance (white arrow in image C) correlates with a cystic component of the mass; E: 6 cm hypodensity with rim enhancement and central hyperdense contents representing post-surgical fluid collection.
- Citation: Abudalou M, Vega EA, Dhingra R, Holzwanger E, Krishnan S, Kondratiev S, Niakosari A, Conrad C, Stallwood CG. Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm-diagnostic approach and post-surgical follow up: Three case reports and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(7): 1682-1695
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i7/1682.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1682