Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2021; 9(7): 1682-1695
Published online Mar 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1682
Published online Mar 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1682
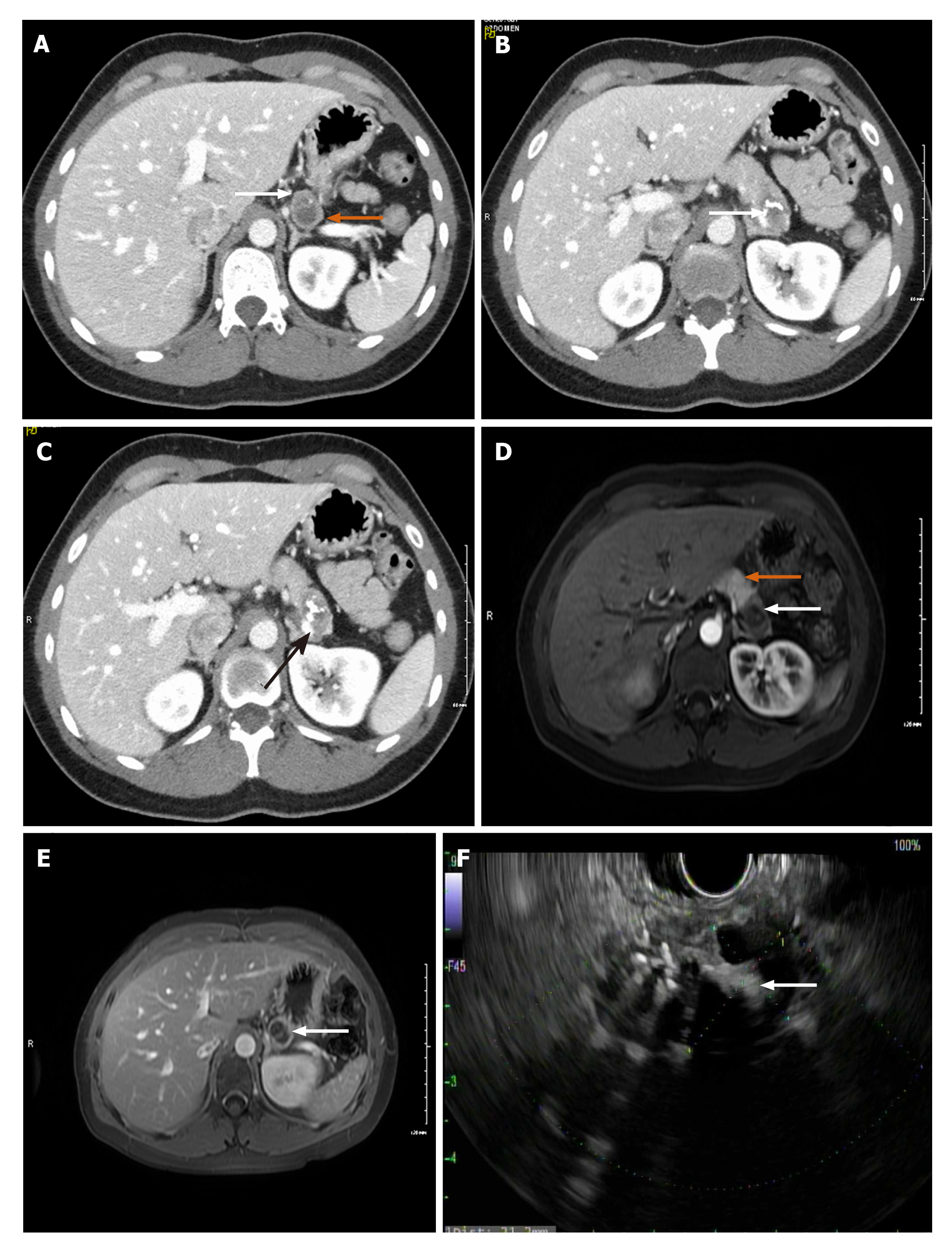
Figure 1 Complex, cystic and solid mass in the pancreatic tail.
A: Axial computed tomography with IV contrast showing a bilobed hypodense lesion with superior and inferior components with peripheral thick rim of enhancement. White arrow: Showing solid component. Orange arrow: Inferior cystic component; B: White arrow: Calcification within tumor; C: Black arrow: Compression of splenic vein by mass effect from tumor; D: Arterial phase magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) image. White arrow: Showing the tumor. Orange arrow: Normal pancreatic tissue; E: MRI post gadolinium study, white arrow: Thick peripheral solid enhancing component with central non-enhancing cystic component with internal septation; F: Solid and cystic mass on endoscopic ultrasound.
- Citation: Abudalou M, Vega EA, Dhingra R, Holzwanger E, Krishnan S, Kondratiev S, Niakosari A, Conrad C, Stallwood CG. Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm-diagnostic approach and post-surgical follow up: Three case reports and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(7): 1682-1695
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i7/1682.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1682