Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2021; 9(7): 1580-1591
Published online Mar 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1580
Published online Mar 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1580
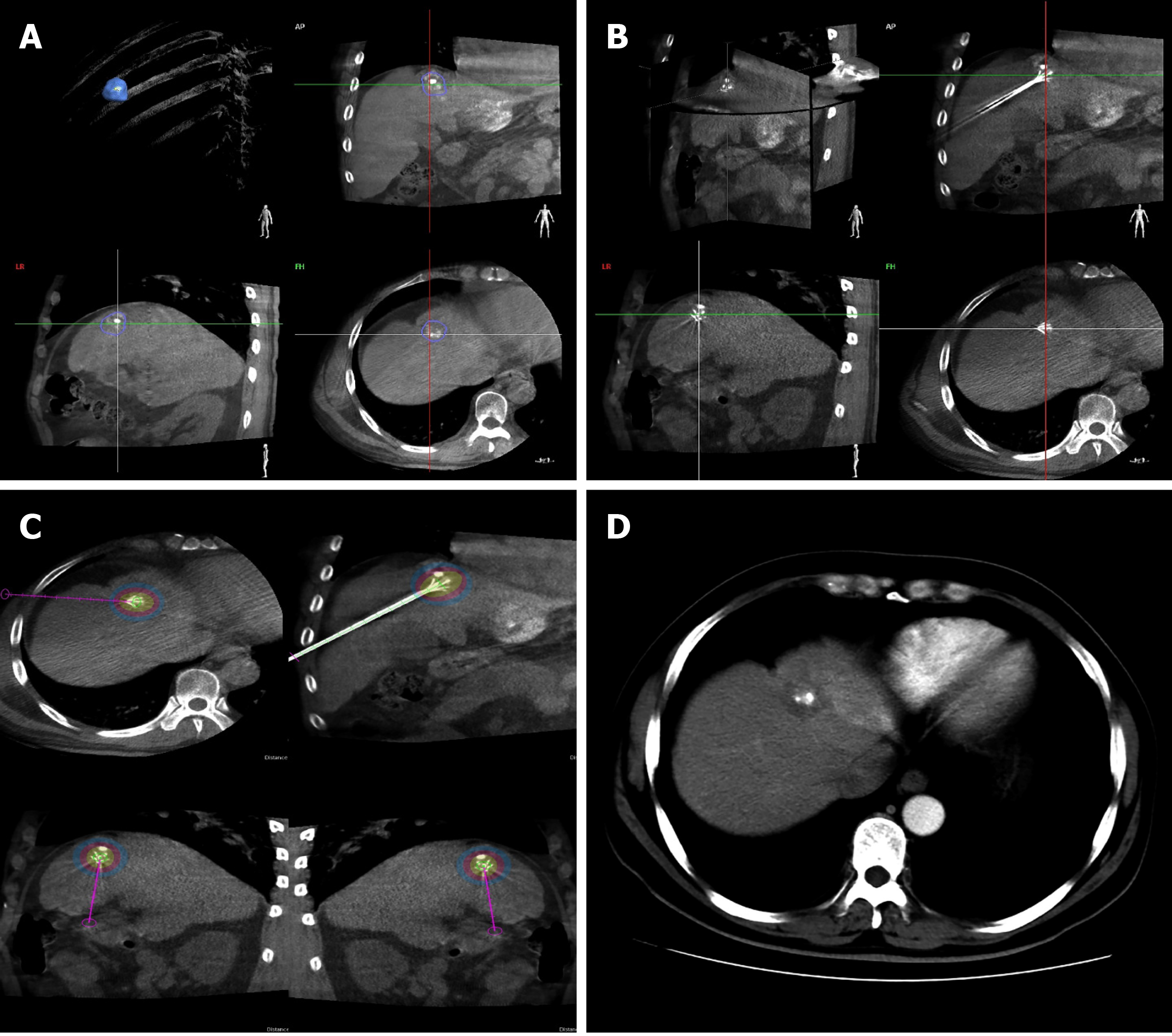
Figure 1 A 37-year-old man with solitary hepatocellular carcinoma < 2 cm in size and close to the diaphragm underwent radiofrequency ablation under cone-beam computed tomography.
A: Semi-automated tumour segmentation was performed during cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) prior to radiofrequency ablation (RFA); B: An ablation needle was inserted following a planned path towards the tumour target and confirmed on the three-dimensional CBCT reconstructed image as well as on the frontal, sagittal, and coronal planes; C: Based on the technical parameters of the ablation needle and equipment, ablation zones associated with various temperature levels were visualized on multiple planes using CBCT planning software; D: Contrast-enhanced CT at 3 mo post-RFA showed complete response and no treatment-related damage to the diaphragm.
- Citation: Yao XS, Yan D, Jiang XX, Li X, Zeng HY, Li H. Short-term outcomes of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma using cone-beam computed tomography for planning and image guidance. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(7): 1580-1591
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i7/1580.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1580