Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 16, 2021; 9(5): 1119-1126
Published online Feb 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i5.1119
Published online Feb 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i5.1119
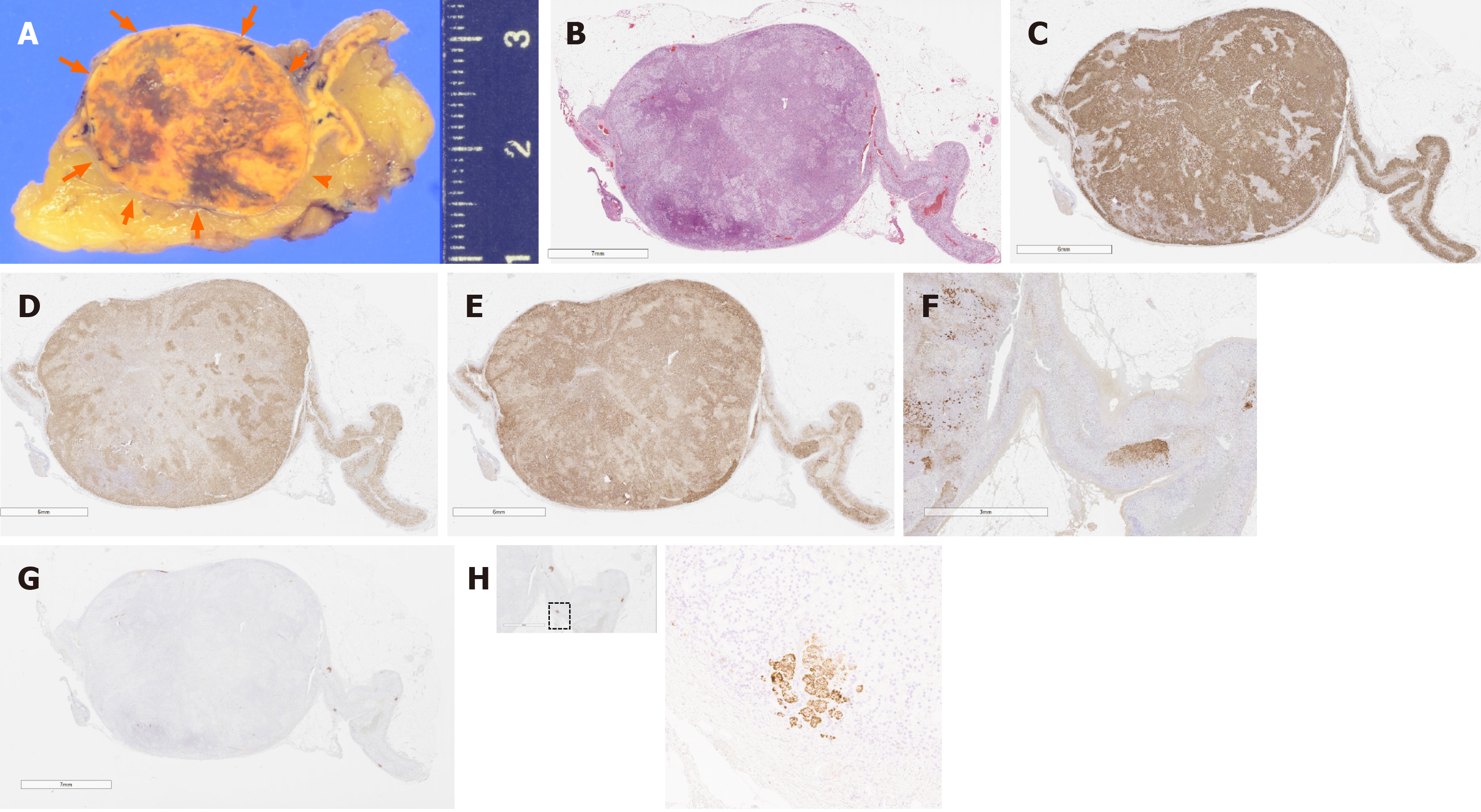
Figure 4 Pathological findings regarding the adrenocortical adenoma and attached adrenal cortex.
A: Cut surface of the tumor and multiple small nodules. The resected tumor (arrows), measuring 2.5 cm × 2.3 cm × 2.0 cm in size, had a heterogeneous yellow and brown appearance. In addition, small cortical nodules less than 3 mm in diameter are also seen; B: Loupe. Upon hematoxylin and eosin staining, the tumor was histopathologically diagnosed as adrenocortical adenoma; C: Loupe. The adrenocortical adenoma was immunohistochemically positive for HSD3B2; D: Loupe. The adrenocortical adenoma was immunohistochemically positive for CYP17A; E: Loupe. The adrenocortical adenoma was immunohistochemically positive for CYP11B1; F: × 10. In the attached adrenal cortex, DHEA-ST expression was reduced, but not by the same extent as that in full-blown Cushing’s syndrome; G: Loupe. CYP11B2 expression was completely negative in the adenoma; H: × 100. In the attached adrenal cortex, there were several aldosterone-producing cell clusters with positive CYP11B2 in the zona glomerulosa.
- Citation: Teragawa H, Oshita C, Orita Y, Hashimoto K, Nakayama H, Yamazaki Y, Sasano H. Primary aldosteronism due to bilateral micronodular hyperplasia and concomitant subclinical Cushing’s syndrome: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(5): 1119-1126
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i5/1119.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i5.1119