Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2021; 9(34): 10451-10463
Published online Dec 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i34.10451
Published online Dec 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i34.10451
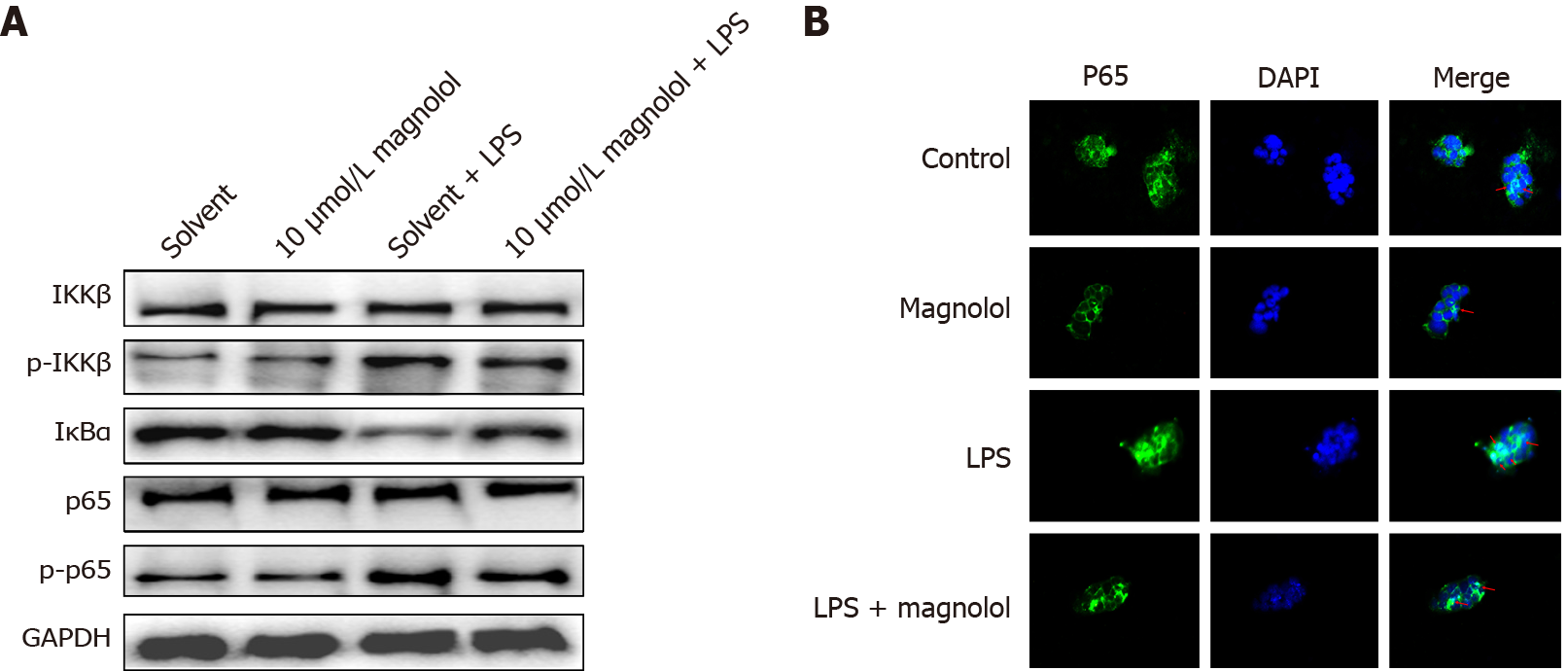
Figure 4 Nuclear factor-kappa B pathway-related protein expression and p65 nucleation in Caco2 cells in each group.
A: The cells were treated with magnolol or solvent for 8 h and then with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (100 μg/mL) for 24 h. The protein levels of phosphorylated inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase β and p65 were assessed by Western blot; B: Fluorescence distribution of p65 in the nucleus of Caco2cells treated with magnolol or solvent for 8 h and then with LPS (100 μg/mL) for 24 h. Control or Solvent: Treated with solvent only; 10 μmol/L magnolol: Treated with 10 μmol/L concentration of magnolol; LPS: Treated with solvent and LPS (100 μg/mL); LPS + magnolol 10 μmol/L: Treated with magnolol 10 μmol/L and with LPS (100 μg/mL); GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DAPI: 4,6-guanidine-2-phenylindole; IKKβ: Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase β; p-IKKβ: Phosphorylated inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase β; IκBα: Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase α; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.
- Citation: Mao SH, Feng DD, Wang X, Zhi YH, Lei S, Xing X, Jiang RL, Wu JN. Magnolol protects against acute gastrointestinal injury in sepsis by down-regulating regulated on activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(34): 10451-10463
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i34/10451.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i34.10451