Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2021; 9(31): 9662-9669
Published online Nov 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i31.9662
Published online Nov 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i31.9662
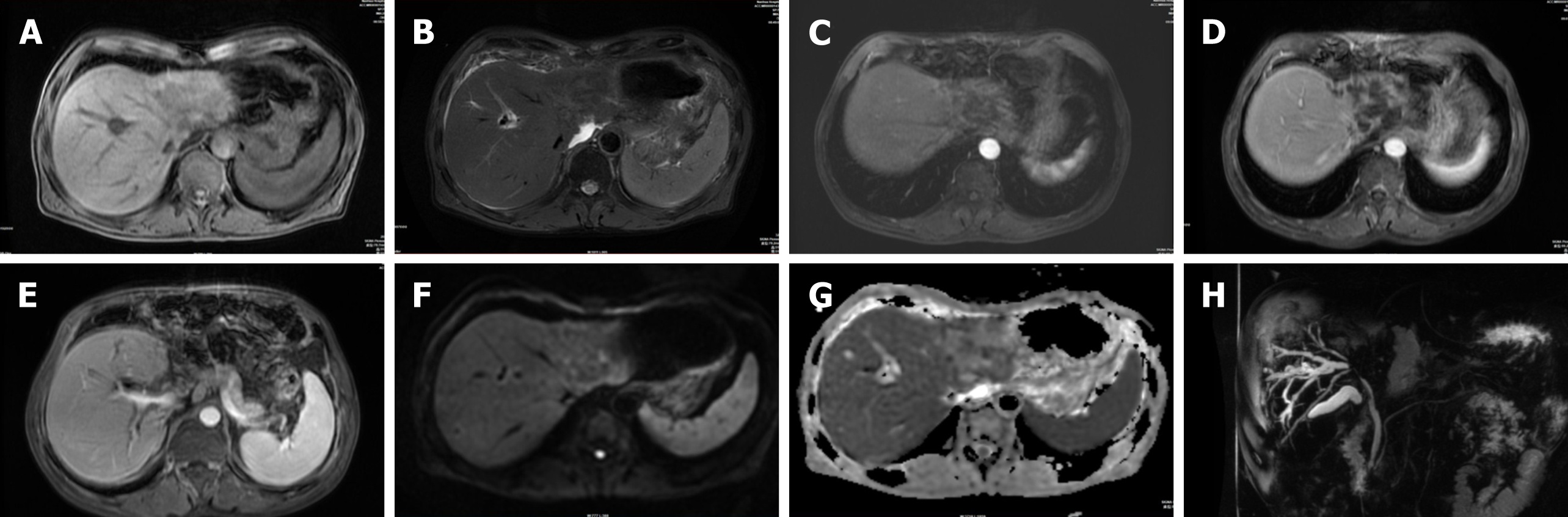
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography scans of hepatic tuberculosis.
A: The lesion showed slightly hypointense signals in T1-weighted images; B: The lesion showed mixed hyperintense and hypointense signals in T2-weighted fat suppressed images; C: The lesion was mildly enhanced at the edge of the arterial phase; D: The margins of the lesion were still mildly enhanced in the portal vein, and no enhancement was seen in the main part of the lesion; E: Premature portal manifestation of the disease was seen in the liver in the arterial phase; F: Mild restricted diffusion was observed; G: The apparent diffusion coefficient value was decreased in the central part of the lesion; H: The left lobe of the liver and the bile ducts in the hilar region were not visualized.
- Citation: Li W, Tang YF, Yang XF, Huang XY. Misidentification of hepatic tuberculosis as cholangiocarcinoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(31): 9662-9669
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i31/9662.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i31.9662