Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2021; 9(30): 8985-8998
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i30.8985
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i30.8985
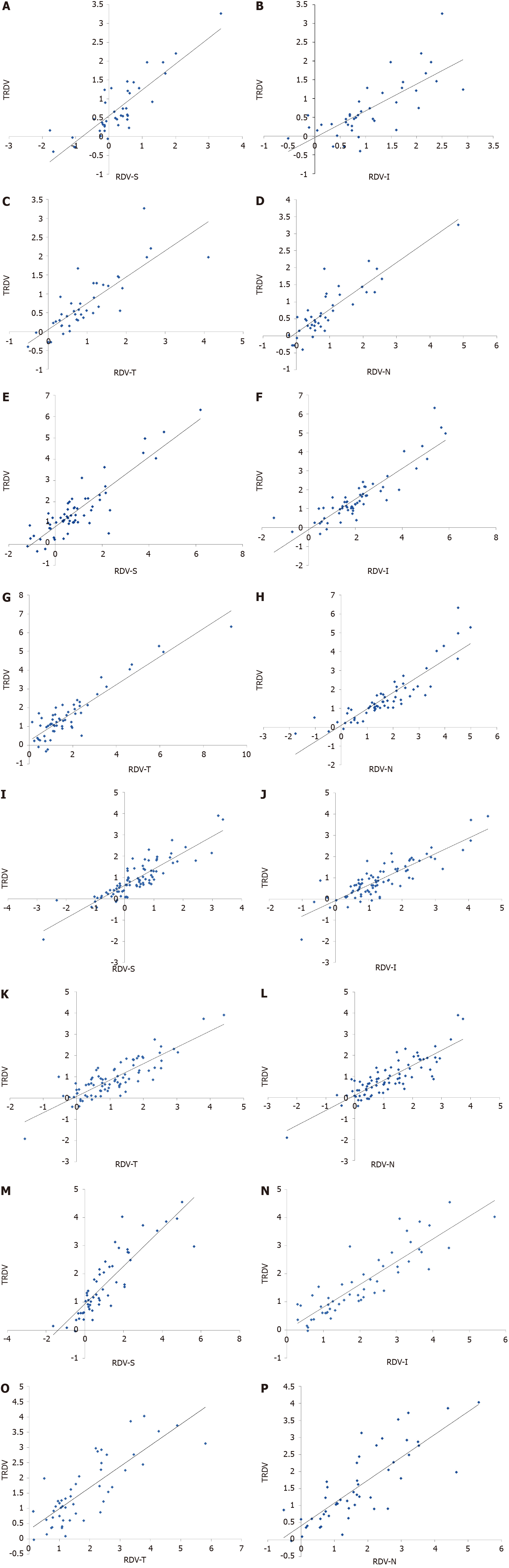
Figure 5 Scatterplots showing the relationship between total retinal defocus value and retinal defocus value of the nasal side of the retina of patients with moderate-degree myopia in group B.
A, E, I, and M: Retinal defocus value of the upper; B, F, J, and N: Retinal defocus value of lower; C, G, K, and O: Retinal defocus value of temporal; D, H, L, and P: Retinal defocus value of nasal. TRDV: Total retinal defocus value; RDV: Retinal defocus value; RDV-S: Retinal defocus value of the upper; RDV-I: Retinal defocus value of lower; RDV-T: Retinal defocus value of temporal; RDV-N: Retinal defocus value of nasal.
- Citation: Ni NJ, Ma FY, Wu XM, Liu X, Zhang HY, Yu YF, Guo MC, Zhu SY. Novel application of multispectral refraction topography in the observation of myopic control effect by orthokeratology lens in adolescents. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(30): 8985-8998
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i30/8985.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i30.8985