Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2021; 9(30): 8985-8998
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i30.8985
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i30.8985
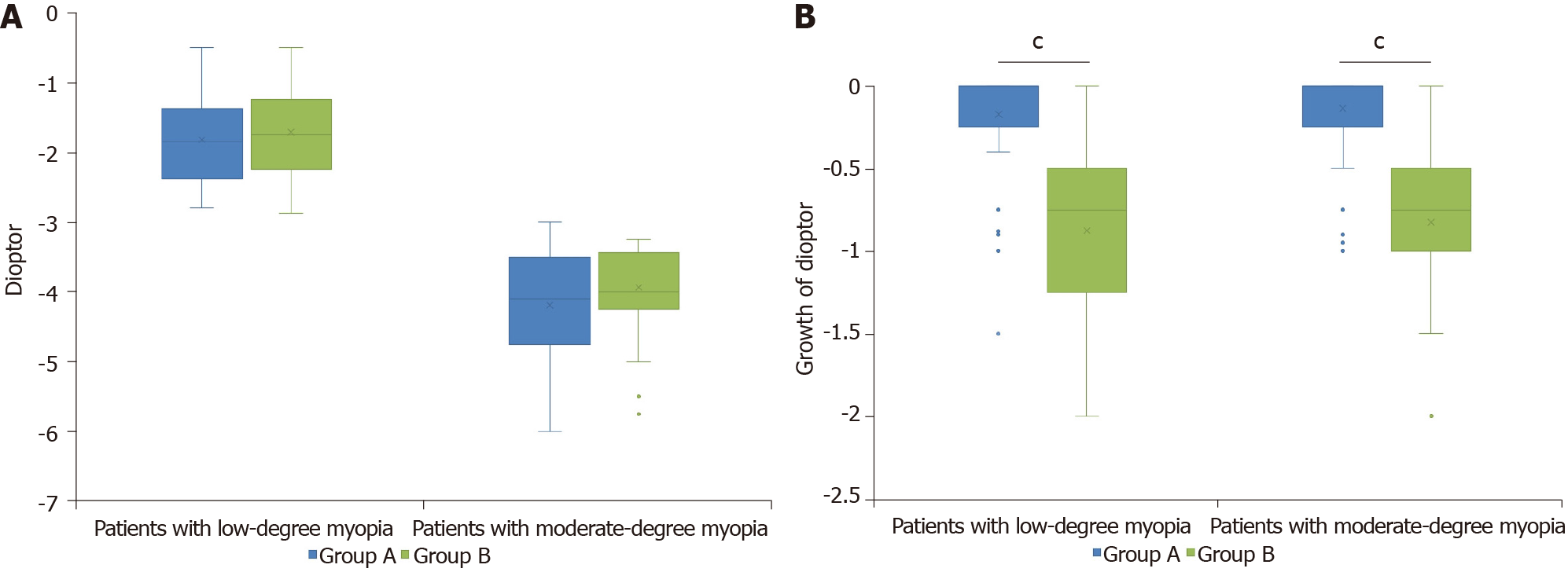
Figure 1 Original diopter values and diopter increase in the two groups.
A: Original diopter values. Of patients with low-degree myopia: Group A: n = 41, mean ± standard deviation (SD) = -1.82 ± 0.71; Group B: n = 59, mean ± SD = -1.71 ± 0.64. Of patients with moderate-degree myopia: Group A: n = 83, mean ± SD = -4.19 ± 0.82; Group B: n = 54, mean ± SD = -3.94 ± 0.62; B: Growth of diopter. Of patients with low-degree myopia: Group A: mean ± SD = -0.17 ± 0.34; Group B: mean ± SD = -0.88 ± 0.39. Of patients with moderate-degree myopia: Group A: mean ± SD = -0.13 ± 0.22; Group B: mean ± SD = -0.82 ± 0.37. N was the number of eyes. Boxes indicate the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd quartile, whiskers represent the maximum and minimum value, and x indicates mean value. Statistically significant differences between patients treated differently were determined by a Mann-Whitney test (cP ≤ 0.001). Group A: Myopia patients wearing orthokeratology lenses for 1 year; Group B: Myopia patients wearing frame glasses.
- Citation: Ni NJ, Ma FY, Wu XM, Liu X, Zhang HY, Yu YF, Guo MC, Zhu SY. Novel application of multispectral refraction topography in the observation of myopic control effect by orthokeratology lens in adolescents. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(30): 8985-8998
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i30/8985.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i30.8985