Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 16, 2021; 9(29): 8906-8914
Published online Oct 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i29.8906
Published online Oct 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i29.8906
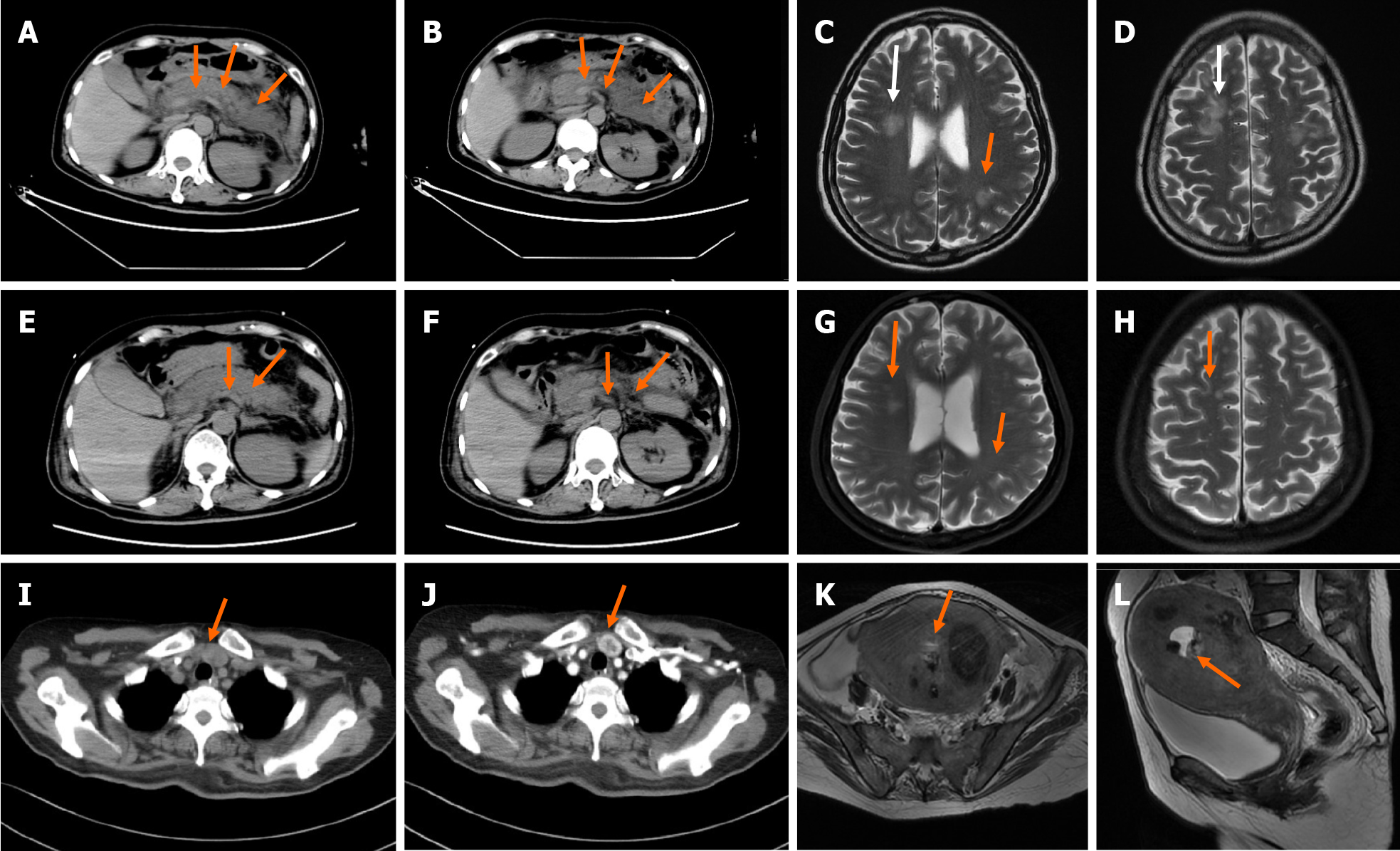
Figure 1 Computed tomography.
A and B: A non-contrast enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen revealed exudation around the pancreas (arrow); C and D: Head magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed abnormal signal in bilateral fronto-parietal-temporal-occipital cortex-medullary junction area and bilateral paraventricular; E-H: A repeated non-contrast enhanced CT scan of the abdomen and head MRI showed reduction of pancreatic exudation and abnormal head signals after effective treatment; I and J: A contrast enhanced CT of the neck showed nodules located on the junction of left lobe of the thyroid and parathyroid gland; K and L: MRI of the pelvis suggested malignant lesions of the uterus and multiple uterine fibroids.
- Citation: Yang L, Lin Y, Zhang XQ, Liu B, Wang JY. Acute pancreatitis with hypercalcemia caused by primary hyperparathyroidism associated with paraneoplastic syndrome: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(29): 8906-8914
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i29/8906.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i29.8906