Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 6, 2021; 9(25): 7391-7404
Published online Sep 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i25.7391
Published online Sep 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i25.7391
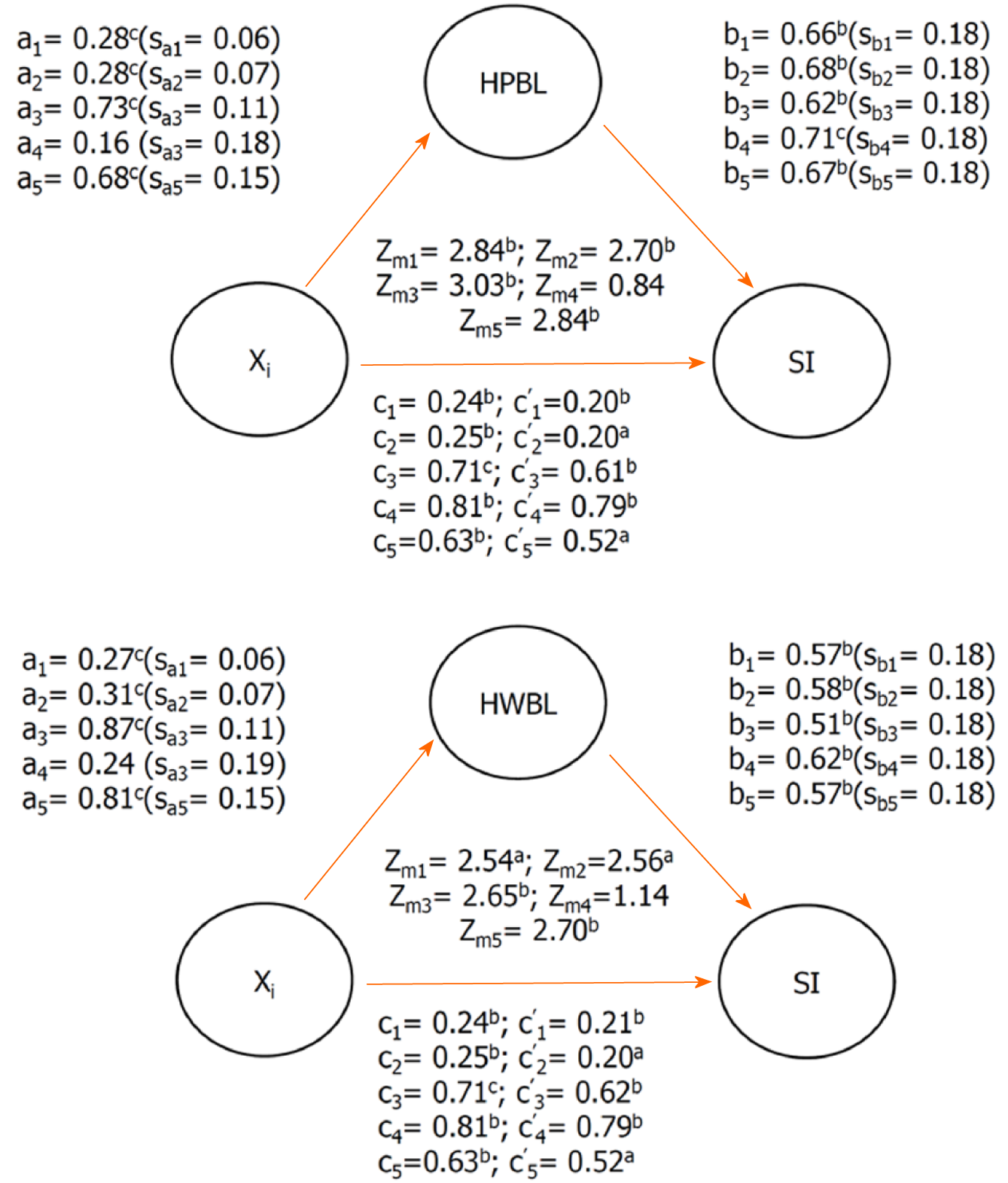
Figure 1 Mediation effects of high personal burnout level/high work-related burnout level in the association between sharps injuries and Xi.
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.0001. 1: Frequent lower limb pain; 2: Frequent upper limb pain; 3: Experience of overtime vs seldom worked overtime; 4: Doctors vs Nurses and others; 5: Irregular work shifts vs other work schedules; ai: The logistic regression coefficient of risk factors for the association between sharps injurie (SI) and risk factors; sai: The standard error of ai; bi: The logistic regression coefficient of burnout as an adjusted variable with regard to the association between SI and Xi; sbi: The standard error of bi. SI: Sharps injurie; HPBL: High personal burnout level; HWBL: High work-related burnout level.
- Citation: Chen YH, Tsai CF, Yeh CJ, Jong GP. Is burnout a mediating factor between sharps injury and work-related factors or musculoskeletal pain? World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(25): 7391-7404
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i25/7391.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i25.7391