Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2021; 9(22): 6544-6551
Published online Aug 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6544
Published online Aug 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6544
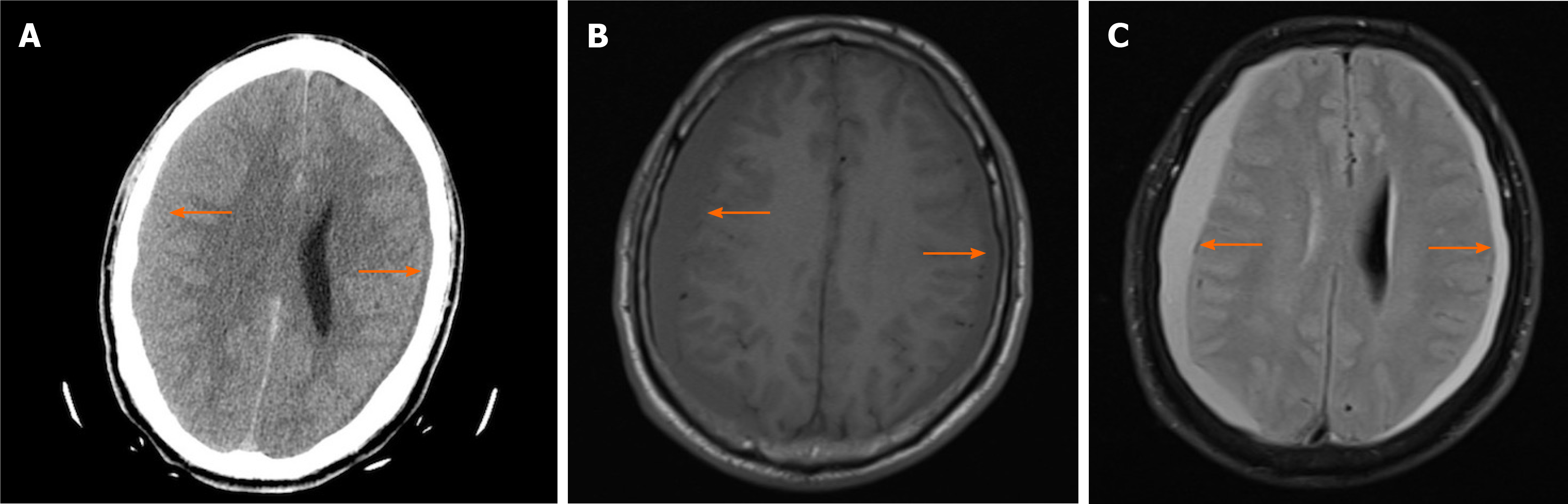
Figure 1 Axial brain image acquired before suspicion of having intracranial hypotension.
A: Axial computed tomography image shows left-sided subdural effusion, right-sided subdural hematoma (orange arrows), compression of the right ventricle and midline shift on day 1; B: Axial T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with gadolinium enhancement reveals diffuse pachymeningeal thickening and subdural hematomas (SDHs) on both sides on day 3 (orange arrows); C: Axial T2-weighted MRI with gadolinium enhancement reveals SDHs with high signal in the same area on day 3 (orange arrows).
- Citation: Wei TT, Huang H, Chen G, He FF. Management of an intracranial hypotension patient with diplopia as the primary symptom: A case report . World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(22): 6544-6551
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i22/6544.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6544