Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2021; 9(22): 6254-6267
Published online Aug 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6254
Published online Aug 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6254
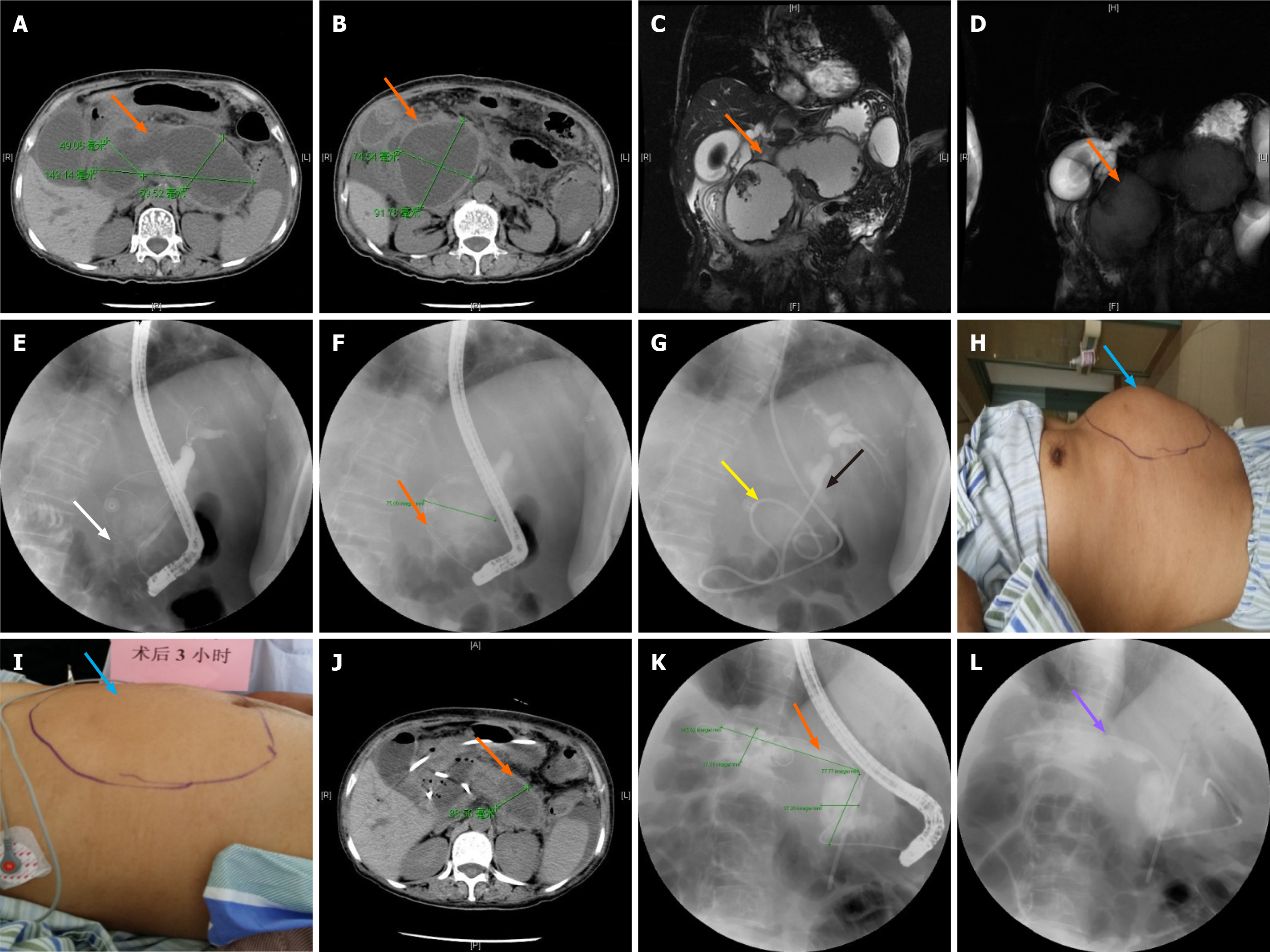
Figure 2 Sequential therapy of pancreatic pseudocysts using the two-step procedure (endoscopic naso-pancreatic drainage combined with endoscopic retrograde pancreatic drainage sequential therapy).
A and B: Location of the pancreatic pseudocyst shown by computed tomography (CT) (orange arrow); C and D: Location of the pancreatic pseudocyst shown by magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (orange arrow) using the T2 weighted image sequence (C) and balanced turbo field echo sequence (D); E: Successful duodenal papilla intubation followed by a guide wire into the pancreatic duct (white arrow); F: Pancreatic pseudocyst shown by imaging of the guide wire into the pancreatic duct (orange arrow); G: Naso-pancreatic duct placed in the pancreatic pseudocyst (yellow arrow is the naso-pancreatic duct, and black arrow is the biliary stent); H: Abdomen of the patient before naso-pancreatic duct placement (blue arrow); I: Changes in the abdomen 3 h after naso-pancreatic duct placement (blue arrow); J: Pancreatic pseudocyst shown by CT 1 wk after naso-pancreatic duct placement (orange arrow); K: Pancreatic pseudocyst shown by guide wire and radiography after removal of the naso-pancreatic duct via endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (orange arrow); L: Placement of the pancreatic duct stent after removal of the naso-pancreatic duct (purple arrow).
- Citation: He YG, Li J, Peng XH, Wu J, Xie MX, Tang YC, Zheng L, Huang XB. Sequential therapy with combined trans-papillary endoscopic naso-pancreatic and endoscopic retrograde pancreatic drainage for pancreatic pseudocysts. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(22): 6254-6267
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i22/6254.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6254