Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2021; 9(22): 6244-6253
Published online Aug 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6244
Published online Aug 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6244
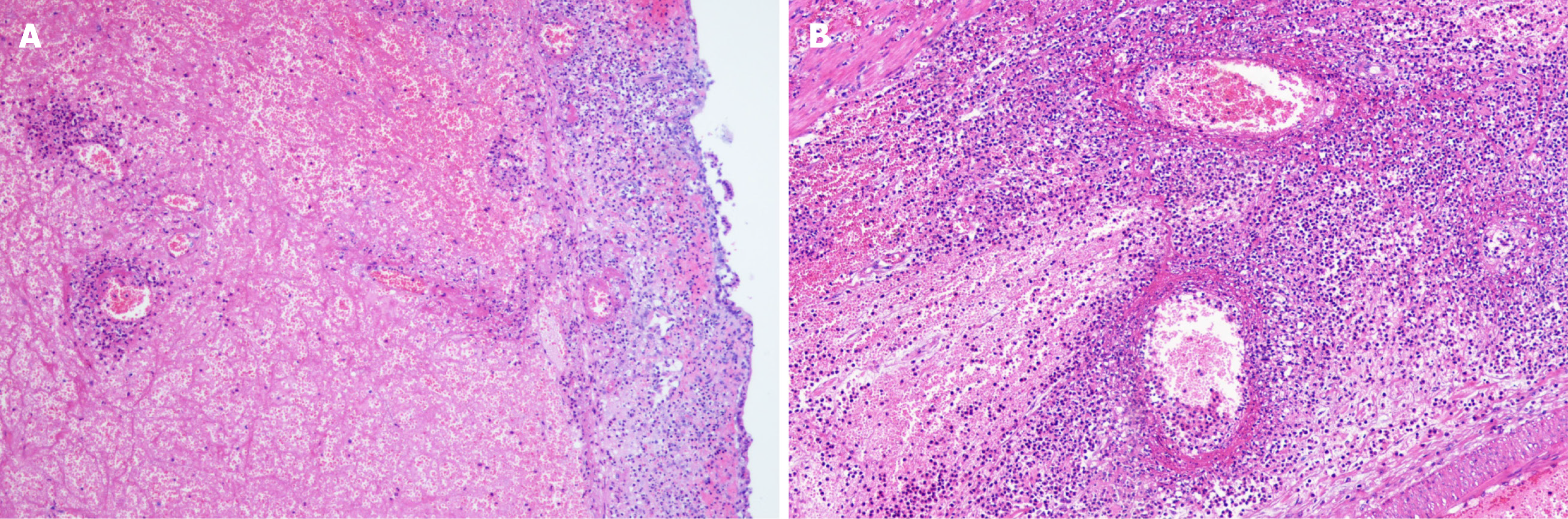
Figure 2 Pathological images of resected intestinal tissue.
A: The intestinal tissue had hyperemia, bleeding, mucosal epithelial necrosis, ulcer formation, granulation tissue hyperplasia, and high submucosal edema; B: The vascular wall was slightly thickened, and some of the vascular wall structure was destroyed. Flake-like infiltration of neutrophils and lymphocytes was observed in the wall and around the small vessel, and many nuclear fragments were observed.
- Citation: Zhao Q, Yang Y, He SW, Wang XT, Liu C. Risk factors for intussusception in children with Henoch-Schönlein purpura: A case-control study. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(22): 6244-6253
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i22/6244.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6244