Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 6, 2021; 9(19): 4890-4917
Published online Jul 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.4890
Published online Jul 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.4890
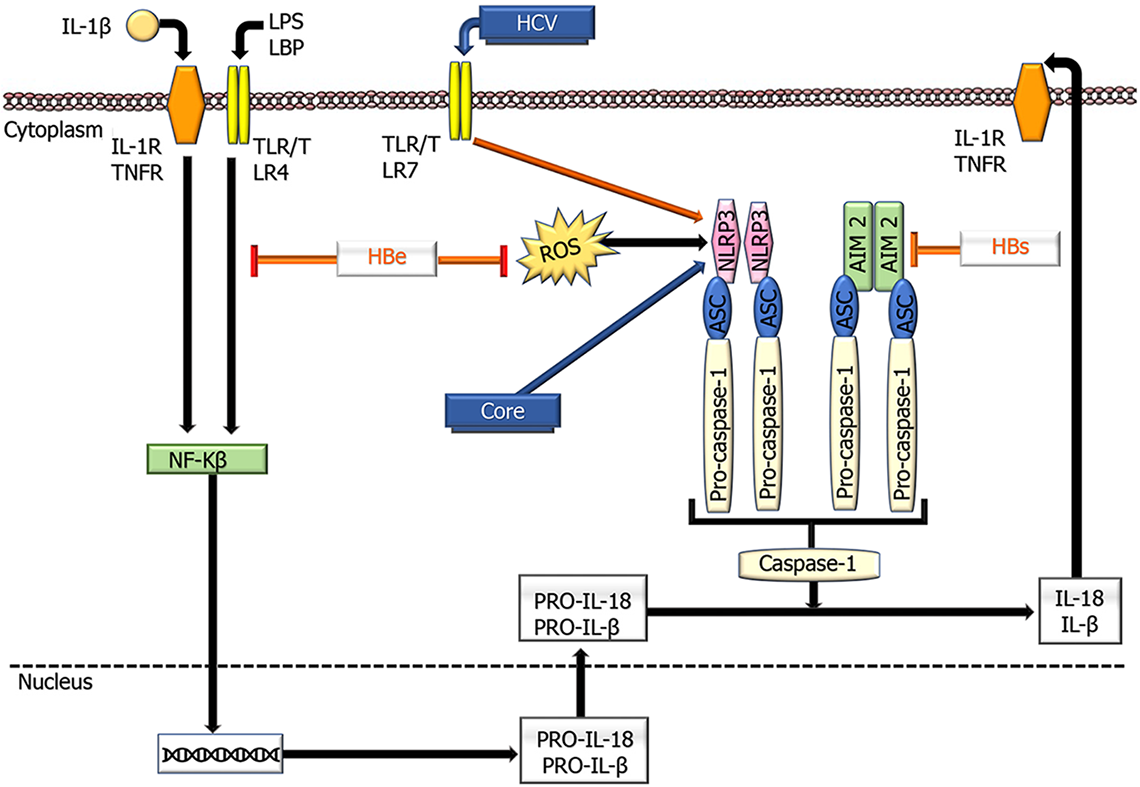
Figure 4 Schematic overview showing the effects of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus proteins on the functioning of NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 and absent in melanoma 2 inflammasomes.
Inflammasome activation is defined by oligomerization of NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 and absent in melanoma 2, which recruits apoptosis-associated speck like proteins and pro-caspase- 1, leading to caspase-1 activation and subsequent conversion of pro-IL- 1β into active IL-1β. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; ASC: Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; AIM2; Absent in melanoma 2; IL: Interleukin; LPS; Lipopolysaccharides; LBP: Lipopolysaccharide binding protein; NLRP3: NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; TLR: Toll-like receptor; TNFR: TNF receptor; ⊥ : Inhibition.
- Citation: Elpek GO. Molecular pathways in viral hepatitis-associated liver carcinogenesis: An update. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(19): 4890-4917
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i19/4890.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.4890