Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 26, 2021; 9(18): 4789-4796
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i18.4789
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i18.4789
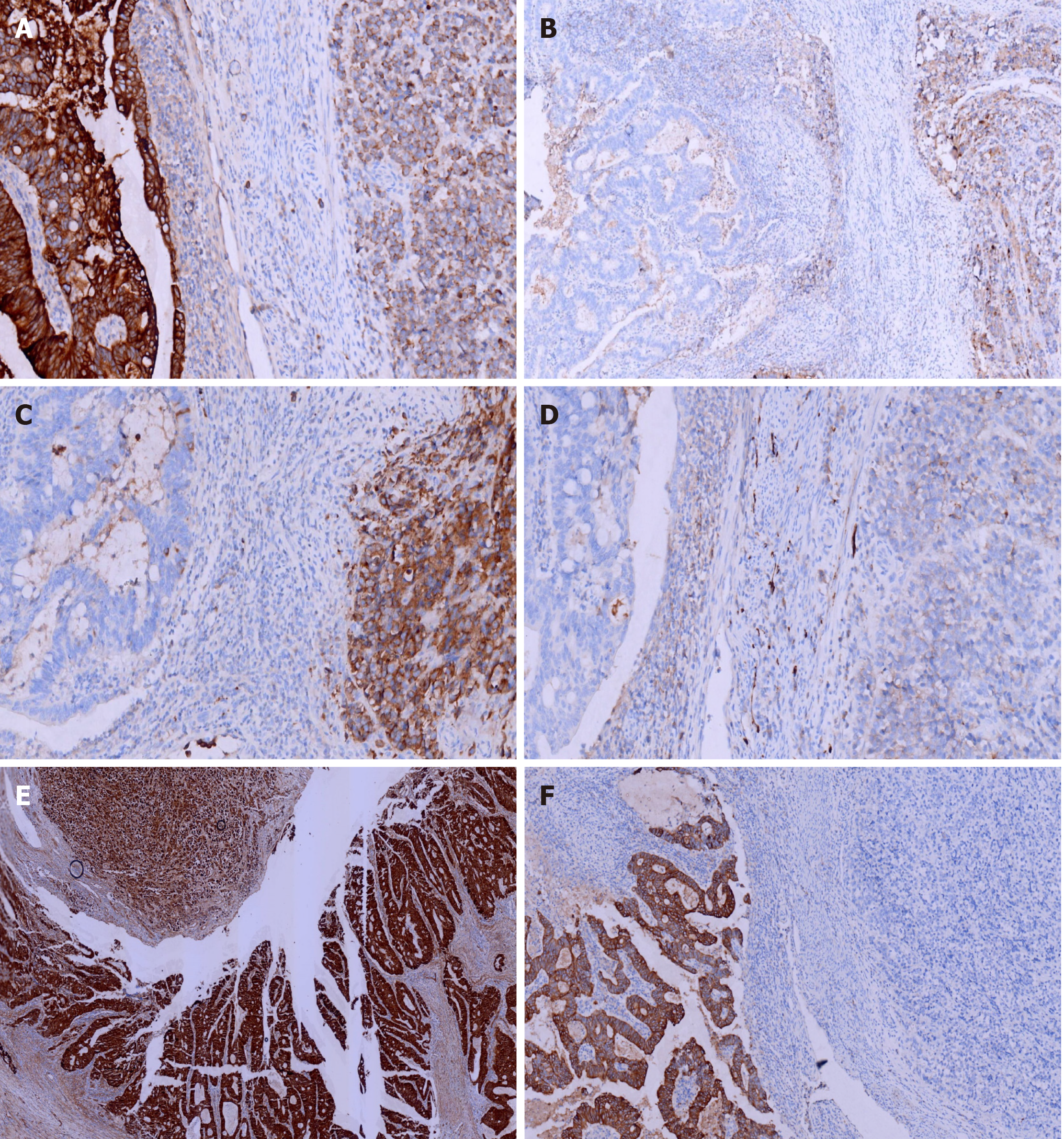
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical staining of cytokeratin, chromogranin A, synaptophysin, and CD56, β-Catenin and CK20.
A: Adenocarcinoma cells were strongly positive for cytokeratin (CK), while neuroendocrine carcinoma cells were weakly positive [immunohistochemistry (IHC) 200 ×]; B: Adenocarcinoma cells were negative for chromogranin A, while neuroendocrine carcinoma cells were positive (IHC 100 ×); C: Adenocarcinoma cells were negative for synaptophysin, while neuroendocrine carcinoma cells were positive (IHC 200 ×); D: Adenocarcinoma cells were negative for CD56, while neuroendocrine carcinoma cells were positive (IHC 200 ×); E: Adenocarcinoma cells were strongly positive for β-Catenin (in the cell membrane) and positive in the cell nucleus of neuroendocrine carcinoma cells (IHC 40 ×); F: Adenocarcinoma cells were strongly positive for CK20, while neuroendocrine carcinoma cells were positive (IHC 100 ×).
- Citation: Zhao X, Zhang G, Li CH. Collision carcinoma of the rectum involving neuroendocrine carcinoma and adenocarcinoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(18): 4789-4796
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i18/4789.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i18.4789