Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 26, 2021; 9(18): 4506-4519
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i18.4506
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i18.4506
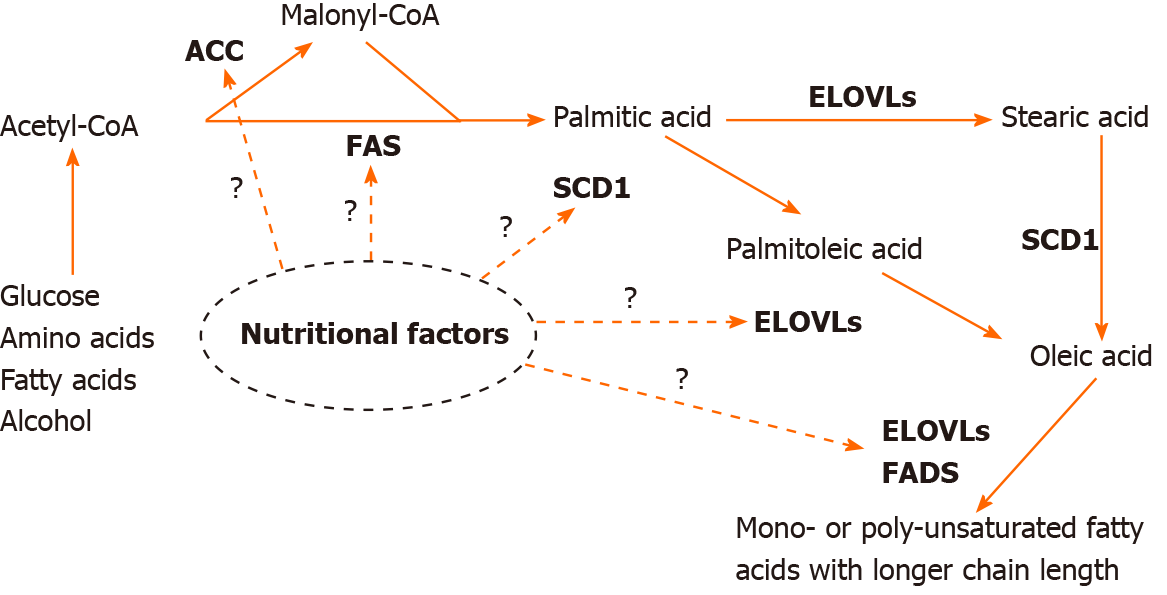
Figure 1 Fatty acid synthesis process in a mammalian cell.
Dietary nutrients are metabolized into acetyl-CoA, which is converted into malonyl-CoA by acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Malonyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA are used by fatty acid synthase to generate palmitic acid, which can be either elongated into stearic acids by elongases (ELOVLs) or desaturated into palmitoleic acid, a monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA), by stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (SCD1). Oleic acid (an MUFA) can be created either via elongation of palmitoleic acid by ELOVLs or desaturation of stearic acid by SCD1. Additional fatty acid with longer chain length or more double bonds can be generated from oleic acid through the activities of ELVOLs and fatty acid desaturases. ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; SCD1: Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1; FADS: Fatty acid desaturases.
- Citation: Yang FC, Xu F, Wang TN, Chen GX. Roles of vitamin A in the regulation of fatty acid synthesis. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(18): 4506-4519
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i18/4506.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i18.4506