Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2021; 9(17): 4381-4387
Published online Jun 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i17.4381
Published online Jun 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i17.4381
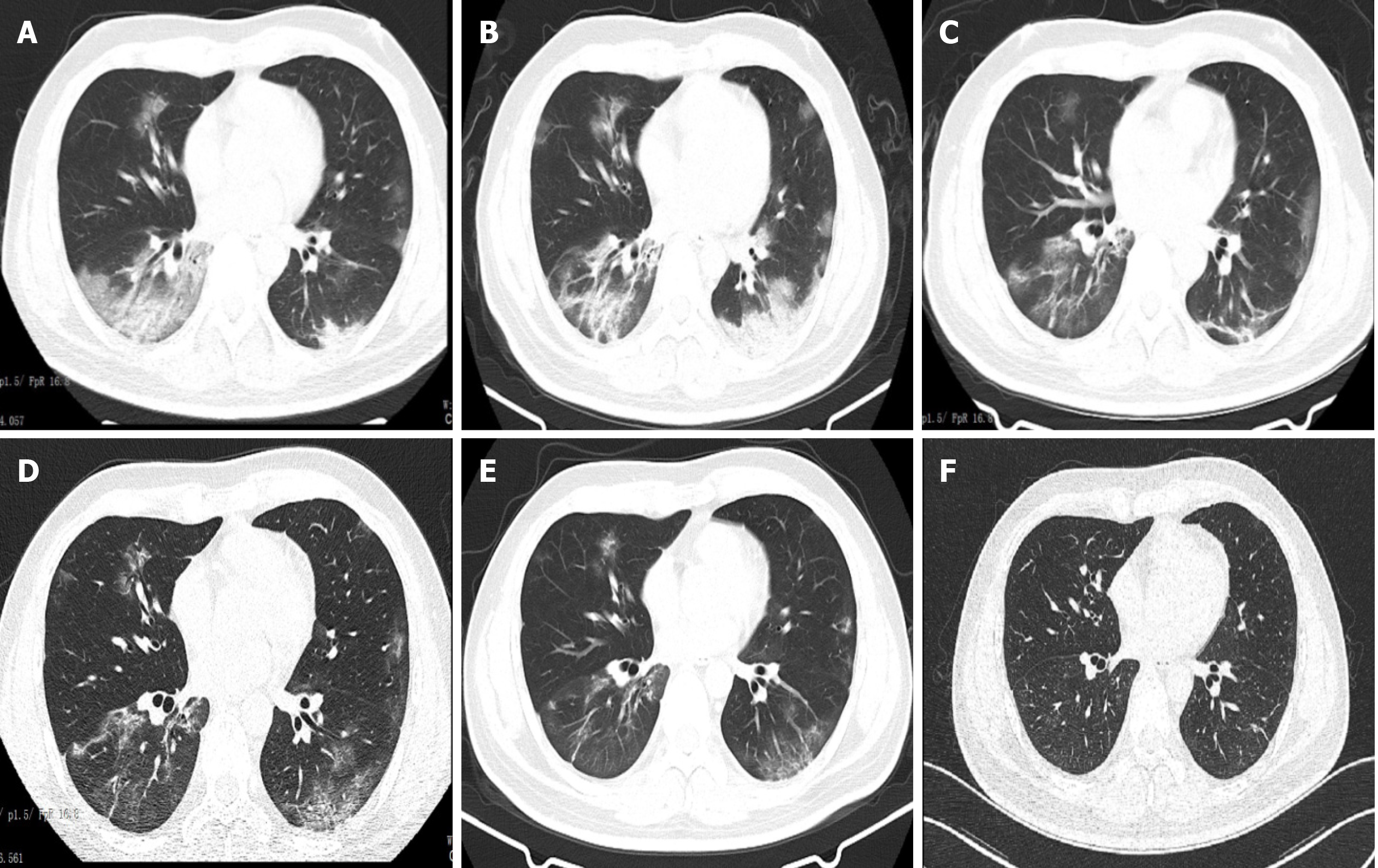
Figure 1 Chest computed tomographic scans in the patient with coronavirus disease 2019.
A: Chest computed tomographic (CT) scan taken on hospital day (HD) 6. It revealed bilateral focal ground-glass opacity associated with consolidation in the right lower lobes; B: Chest CT scan taken on HD 9 [3 d after prone position (PP) and conventional oxygen therapy]. It revealed consolidation in the right and left lower lobes; C and D: Chest CT scans taken on HDs 12 and 15, respectively. They revealed ground-glass opacities and consolidations being dissipated during the PP and high-flow nasal oxygen therapy; E: Chest CT scan taken on HD 21. It revealed further resolution of the lesions; F: Chest CT scan taken on follow-up. It was normal.
- Citation: Xu DW, Li GL, Zhang JH, He F. Prone position combined with high-flow nasal oxygen could benefit spontaneously breathing, severe COVID-19 patients: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(17): 4381-4387
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i17/4381.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i17.4381