Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 26, 2021; 9(12): 2711-2720
Published online Apr 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i12.2711
Published online Apr 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i12.2711
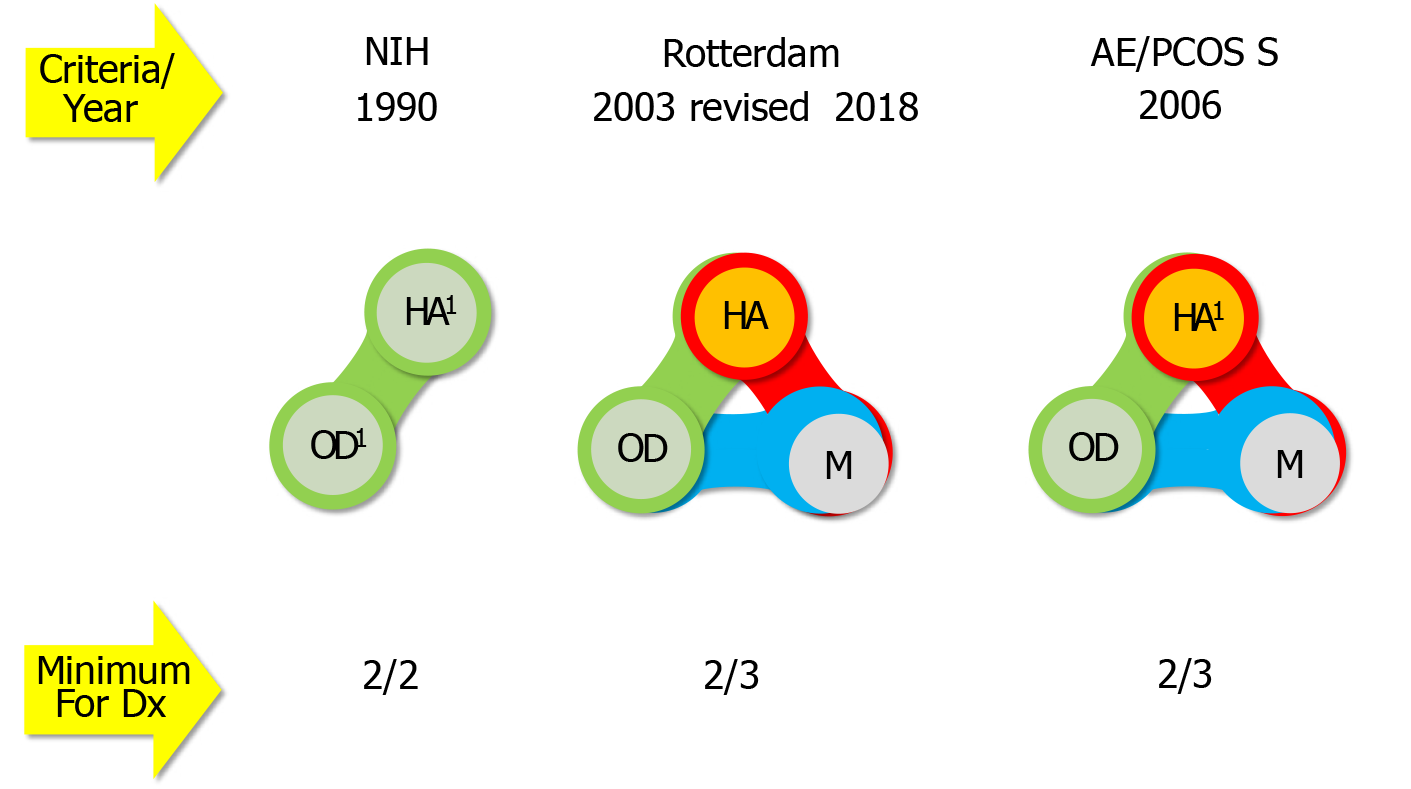
Figure 1 Criteria for defining polycystic ovary syndrome and describing its phenotypes (summarized from[5-7]).
1Sine qua non for diagnosis, when excluding all similar/mimicking disorders after thorough laboratory and instrumental investigations. NIH: National Institutes of Health (United States) criteria; Rotterdam: European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology/American Society for Reproductive Medicine criteria; AE/PCOS S: Androgen Excess and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Society criteria; HA: Hyperandrogenism; OD: Ovulatory dysfunction; M: Polycystic ovary morphology: At least one ovary with volume > 10 cm3 or at least 12-20 antral follicles (with a diameter of 5-9 mm) per ovary; Dx: Diagnosis.
- Citation: Ilias I, Goulas S, Zabuliene L. Polycystic ovary syndrome: Pathways and mechanisms for possible increased susceptibility to COVID-19. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(12): 2711-2720
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i12/2711.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i12.2711