Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 16, 2021; 9(11): 2662-2670
Published online Apr 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2662
Published online Apr 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2662
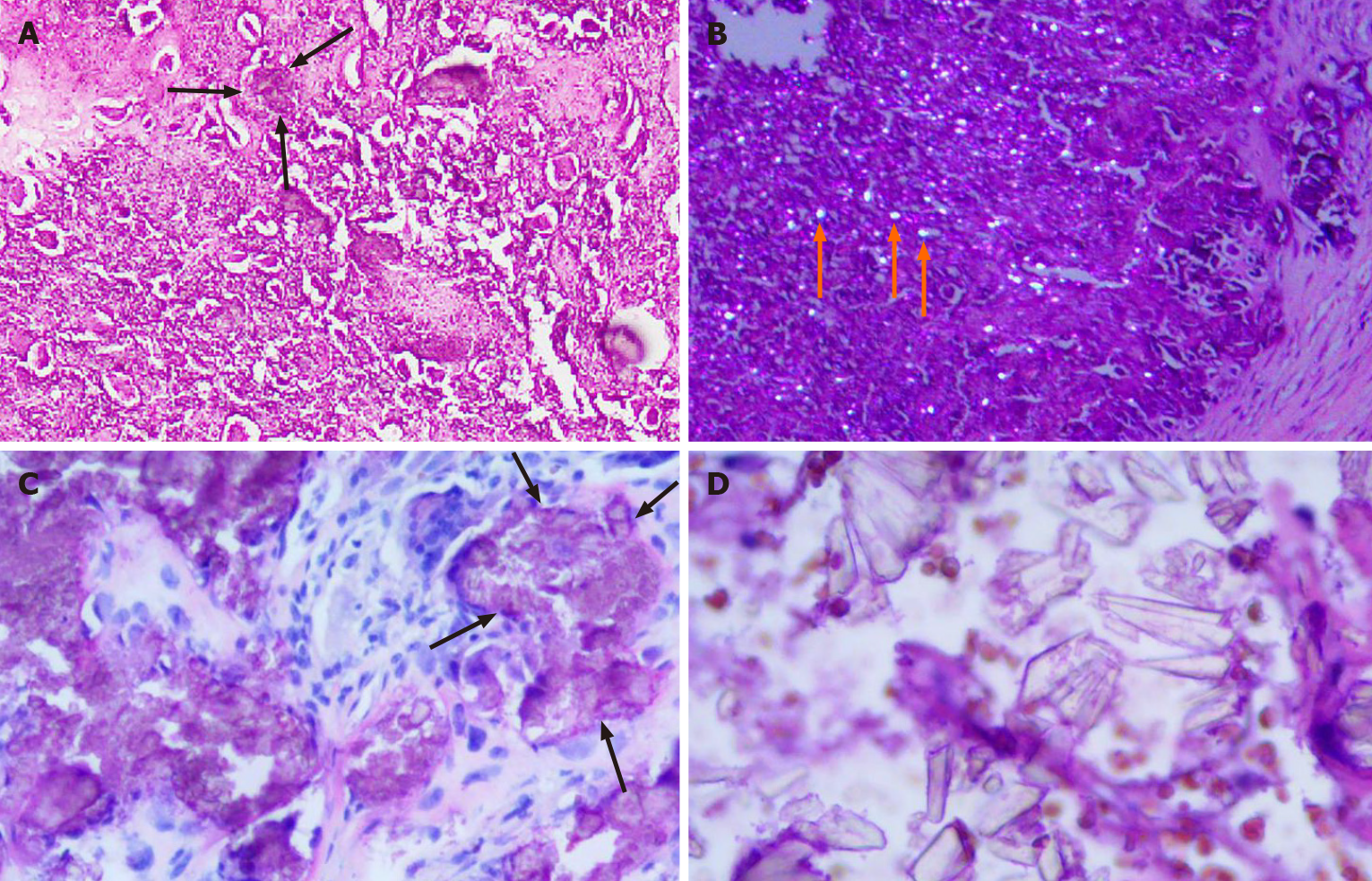
Figure 4 Histopathology of Case 1 and Case 2.
A: There are crystal deposits (black arrows) in the fibrous tissue. The crystal deposits are surrounded by foreign body type giant cells and fibroblasts (hematoxylin-eosin staining, × 100; Case 1); B: Crystalline material (orange arrows) deposits exhibiting birefringence under polarized light (hematoxylin-eosin staining, × 100; Case 1); C: Nodular clusters of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals (black arrows) could be seen (hematoxylin-eosin staining, × 200; Case 2); D: Crystals of different shapes with strong stereoscopic effect (hematoxylin-eosin staining, × 400; Case 2).
- Citation: Tang T, Han FG. Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease of the temporomandibular joint invading the middle cranial fossa: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(11): 2662-2670
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i11/2662.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2662