Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 16, 2021; 9(11): 2555-2561
Published online Apr 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2555
Published online Apr 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2555
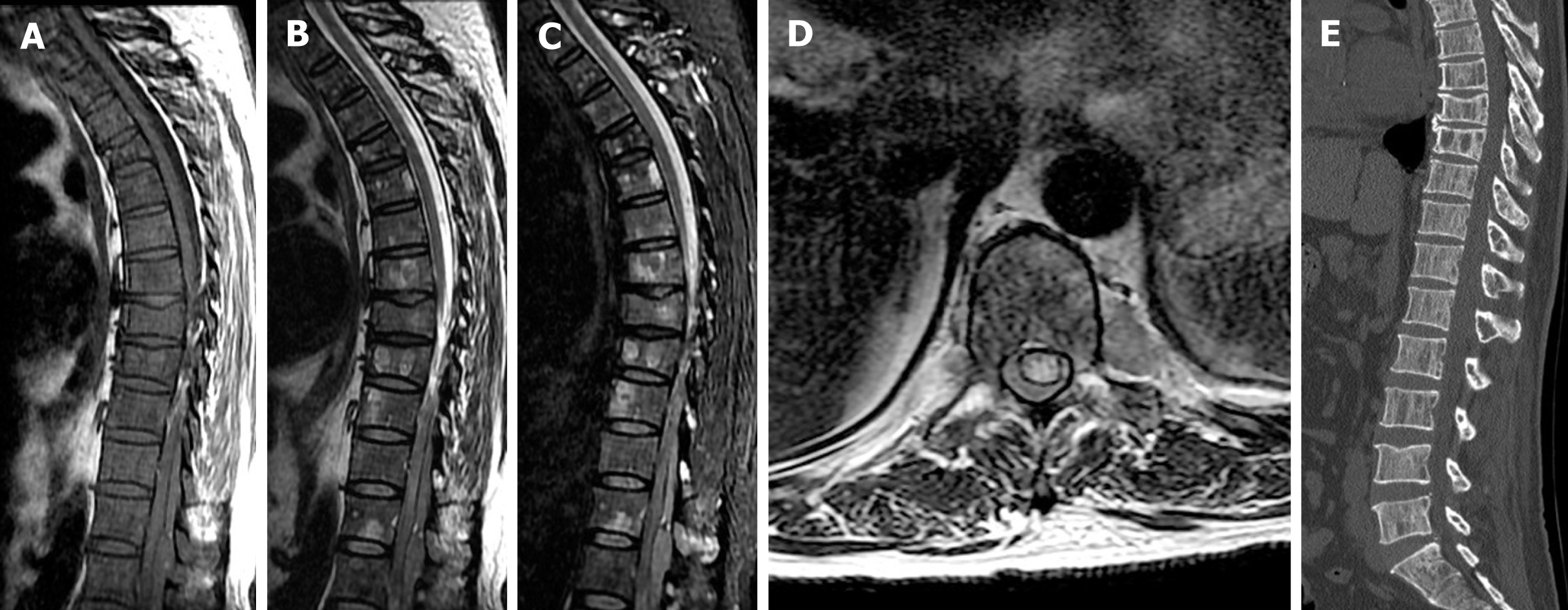
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging showed a posterior epidural mass located from Th11 to L1.
A: Sagittal T1-weighted imaging (T1WI); B: T2-weighted imaging (T2WI); C: T2-weighted fat-saturation imaging; and D: Axial T2WI showing an epidural mass compressing the spinal cord. Diffuse patchy areas of isointense signal on T1WI and slightly hyperintense signal on T2WI were seen in all vertebrae; E: Computed tomography showed multifocal osteolysis and clearly defined cortical margins of the vertebrae from Th11 to L1. The Th8 and Th9 vertebral bodies had collapsed, indicating a compression fracture caused by myeloma-induced bony destruction.
- Citation: Cui JF, Sun LL, Liu H, Gao CP. Extraosseous spinal epidural plasmocytoma associated with multiple myeloma: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(11): 2555-2561
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i11/2555.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2555