Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 16, 2021; 9(11): 2555-2561
Published online Apr 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2555
Published online Apr 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2555
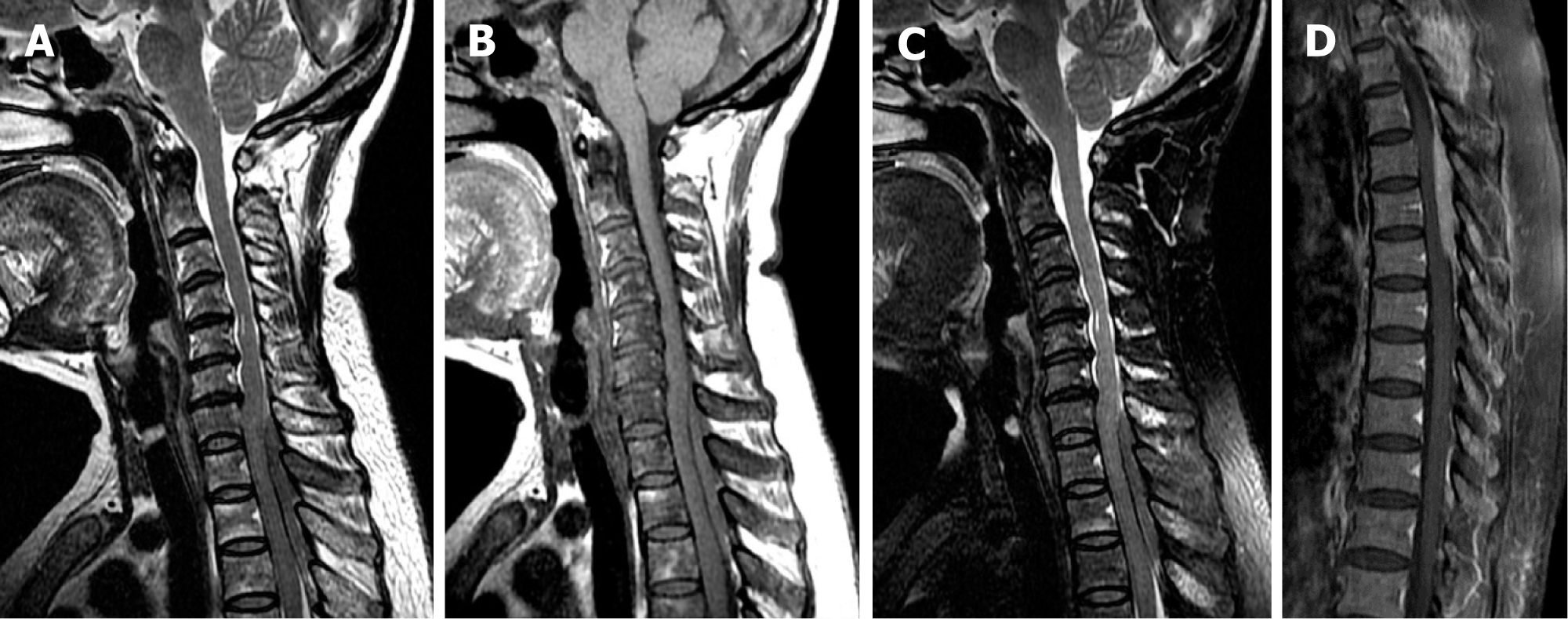
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging showed a posterior spinal epidural mass located from C7 to T3.
A: T1-weighted imaging (T1WI); B: T2-weighted imaging (T2WI); C: T2-weighted fat-saturation imaging; D: Sagittal T1WI of the spine with contrast. The lesion appeared isointense on T1WI, T2WI, and T2-weighted fat-saturation imaging. The spinal cord was significantly compressed, and the dural sac between the mass and spinal cord showed a hypointense signal on all sequences, indicating an extradural tumor location. T1WI showing decreased marrow signal intensity in the vertebrae, suggesting diffuse marrow infiltration. Sagittal T1WI of the spine with contrast showing anterior displacement of the spinal cord with moderate enhancement of the mass.
- Citation: Cui JF, Sun LL, Liu H, Gao CP. Extraosseous spinal epidural plasmocytoma associated with multiple myeloma: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(11): 2555-2561
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i11/2555.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2555