Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 6, 2021; 9(10): 2400-2408
Published online Apr 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2400
Published online Apr 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2400
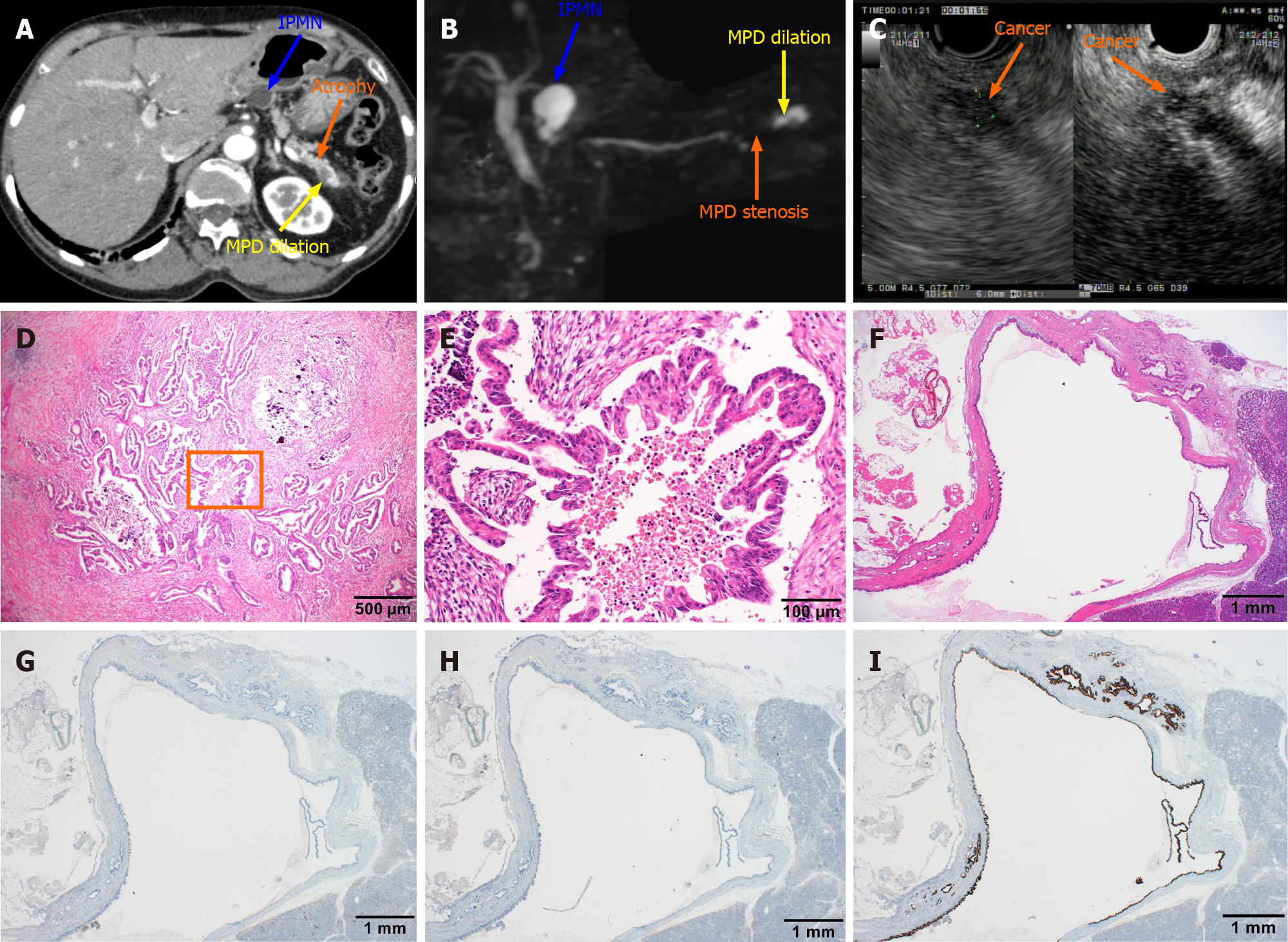
Figure 2 Computed tomography, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, and endoscopic ultrasound images obtained after admission and postoperative pathological diagnosis.
A: The blue arrow indicated a lesion of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) with a circular low-density shadow of the pancreatic body with clear boundaries. The orange arrow indicates atrophy in the tail of the pancreas with decreased density. The yellow arrow indicates local dilation of the pancreatic duct in the tail of the pancreas; B: The blue arrow indicates a lesion of IPMN with a high signal of the pancreatic body, which communicated with the pancreatic duct. The orange arrow indicates pancreatic duct stenosis in the tail of the pancreas. The yellow arrow points to local dilation of the pancreatic duct in the tail of the pancreas; C: The endoscopic ultrasound dynamic scan shows a dilated caudal pancreatic duct with a hypoechoic mass at the root of the dilatation, with uneven internal echogenicity and unclear borders. The orange arrow points to the hypoechoic mass on contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound angiography, suggesting a high probability of pancreatic cancer; D: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the pancreatic tissue section shows dendritic and papillary growth of pancreatic cancer associated with localized calcification; E: At high magnification, cancer cells show the papillary proliferation with necrosis at the center marked inside panel D; F: The histological features of IPMN are cystic lesion composed of dilated ducts and with the cystic surface lined by a layer of columnar epithelial cells, with basal nuclei showing minimal atypia; G-I: Serial sections were also immunohistochemically stained with antibodies against mucin (MUC) 1 (G) , MUC2 (H) and MUC5AC (I), but only MIC5AC was positively stained. IPMN: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; MPD: Methylpentedrone.
- Citation: Ma YH, Yamaguchi T, Yasumura T, Kuno T, Kobayashi S, Yoshida T, Ishida T, Ishida Y, Takaoka S, Fan JL, Enomoto N. Pancreatic cancer secondary to intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm with collision between gastric cancer and B-cell lymphoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(10): 2400-2408
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i10/2400.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2400