Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 6, 2021; 9(1): 71-80
Published online Jan 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.71
Published online Jan 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.71
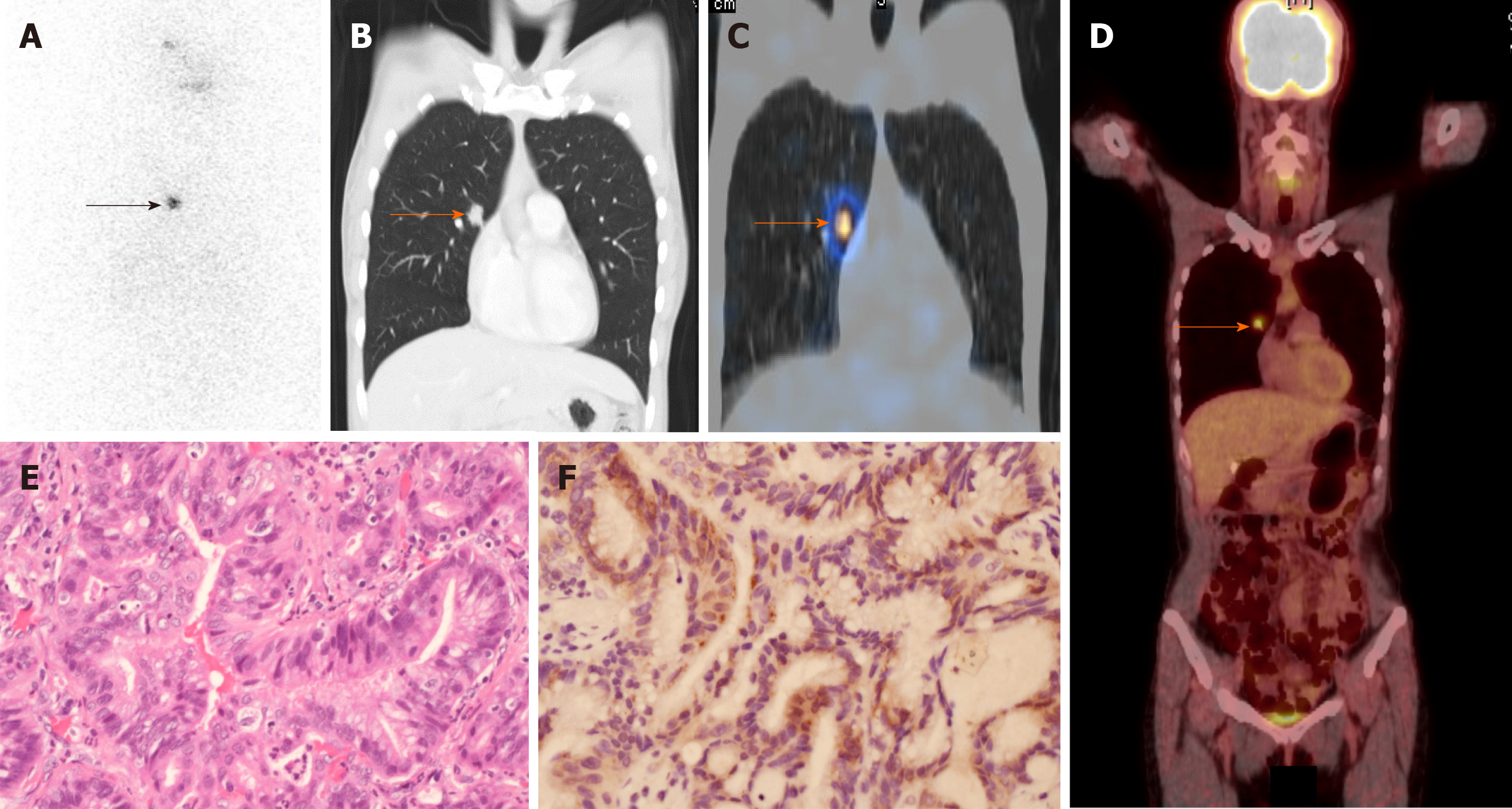
Figure 2 Details of patient 1.
A: Radioiodine scan was performed 7 d after oral administration of 30 mCi iodine-131. Radioiodine uptake was identified in the right chest (black arrow); B: Computed tomography revealed a single 1.7-cm spiculated nodule in the right upper lobe (orange arrow); C: Fused single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography imaging demonstrated a focal area of radioiodine activity in the right lung tumor (orange arrow); D: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) positron emission tomography/computed tomography showed that the lung tumor was 18FFDG avid (orange arrow); E: Histopathologic features of the right lung tumor were consistent with lung adenocarcinoma (hematoxylin and eosin staining, 200 ×); F: Immunostaining for sodium/iodide symporter (NIS) showed NIS expression in lung adenocarcinoma cells (brown; 200 ×).
- Citation: Lu YL, Chen ST, Ho TY, Chan WH, Wong RJ, Hsueh C, Lin SF. Primary lung cancer with radioiodine avidity: A thyroid cancer cohort study. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(1): 71-80
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i1/71.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.71