Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 6, 2021; 9(1): 190-196
Published online Jan 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.190
Published online Jan 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.190
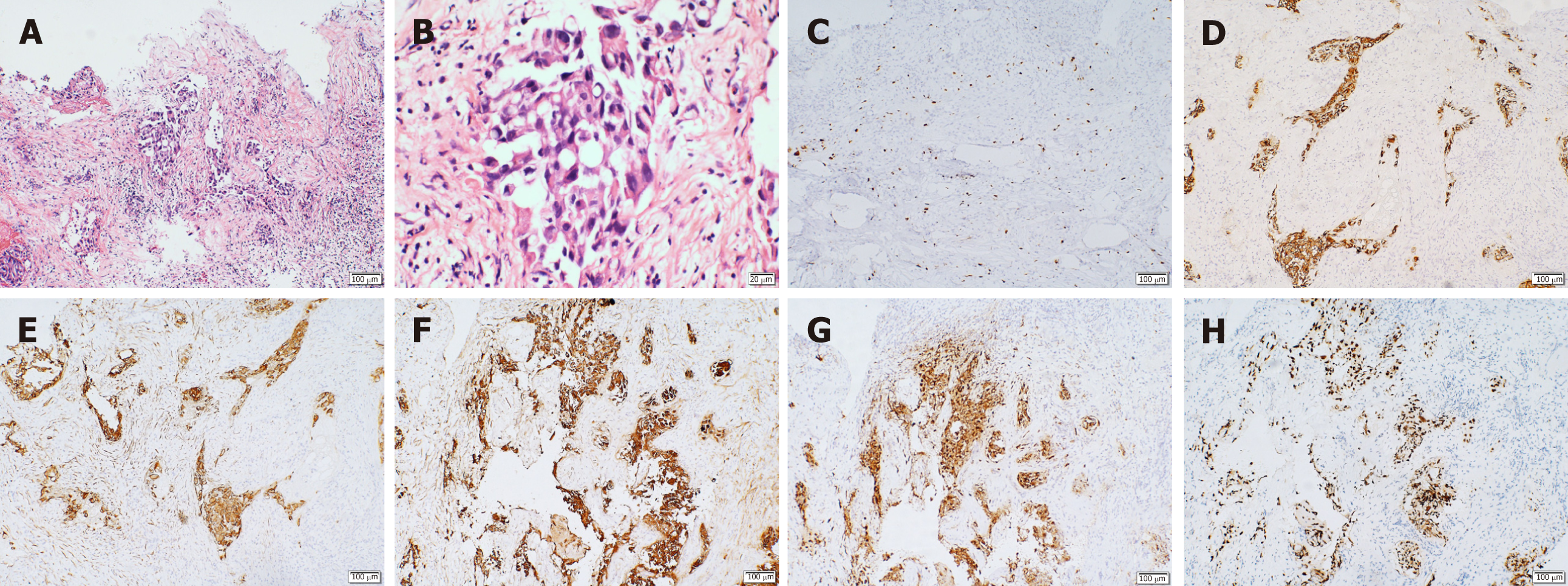
Figure 2 Immunohistochemistry results.
A: Increased nucleus and mitosis (hematoxylin and eosin × 10); B: Low differentiation and increased mucus secretion (positive hematoxylin and eosin × 40); C: Ki-67, suggestive of active cell proliferation and low degree of differentiation; D: Cytokeratin (CK)-positive, suggestive of epithelial cell differentiation, and thus, supporting the diagnosis of lung cancer metastasis; E: CK7 (+), supporting the diagnosis of lung cancer; F: CK-pan (+), suggesting that the tissue originated from epithelial cells; G: napsin A (+), suggestive of primary lung adenocarcinoma; H: thyroid transcription factor 1 (+), suggestive of non-small cell lung cancer.
- Citation: Liu CY, Wang YB, Zhu HQ, You JL, Liu Z, Zhang XF. Hyperprolactinemia due to pituitary metastasis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(1): 190-196
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i1/190.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.190