Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2020; 8(23): 5902-5917
Published online Dec 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i23.5902
Published online Dec 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i23.5902
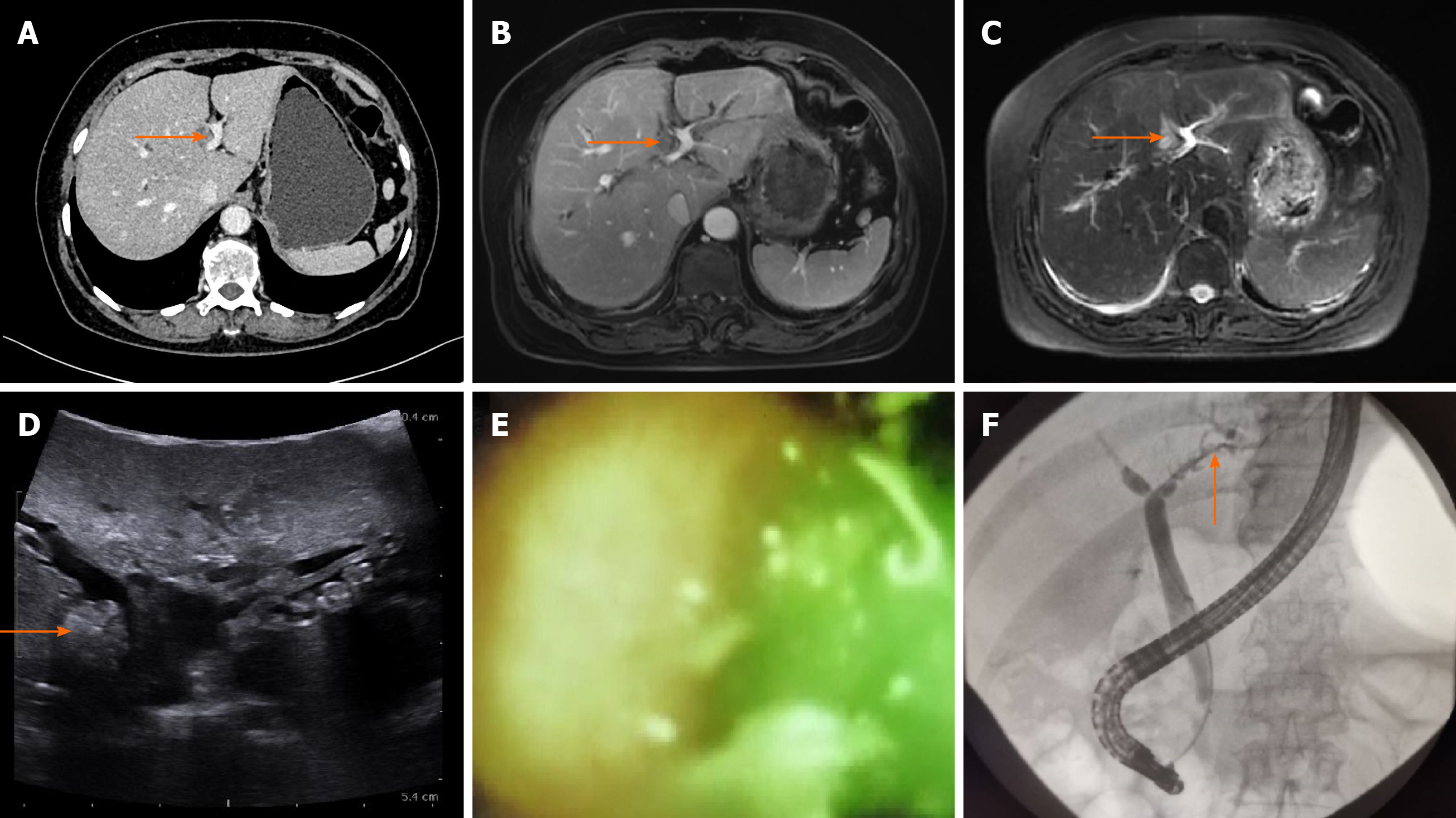
Figure 4 Multidetector-row computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography images of patient No.
4. A: The orange arrow in the computed tomography scan image shows dilated B4; B and C: T1- (B) and T2-weighted (C) magnetic resonance imaging scans show low and high signals in B4, respectively; D: The ultrasound shows a 1.0 cm × 1.0 cm mass-like high-echo lesion in B4 (orange arrow); E and F: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with SpyGlass failed to enter B4 but detected small stones and batt-like exudate in the peripheral part of the left hepatic duct.
- Citation: Zhou D, Zhang B, Zhang XY, Guan WB, Wang JD, Ma F. Focal intrahepatic strictures: A proposal classification based on diagnosis-treatment experience and systemic review. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(23): 5902-5917
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i23/5902.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i23.5902