Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2020; 8(20): 4773-4784
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.4773
Published online Oct 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.4773
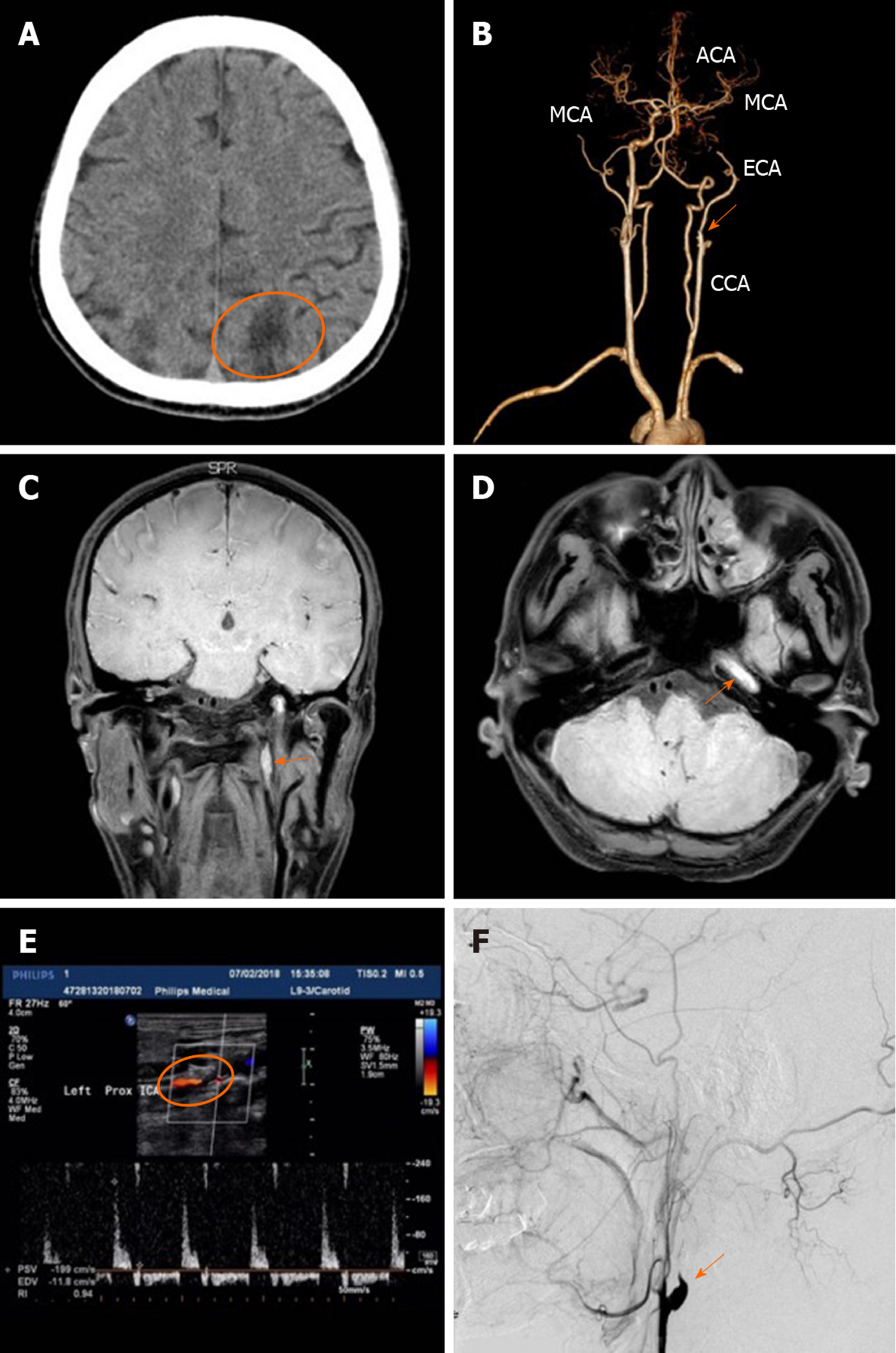
Figure 2 Imaging of case 1.
A: Computed tomography revealed left parietal infarction (ellipse); B: Computed tomography angiography examination revealed tapering occlusion of the Internal carotid artery (ICA) suggestive of ICA dissection (arrow); C and D: Magnetic resonance imaging (T1W-VISTA sequence) demonstrated an intimal intramural hematoma extending to the intracranial section (arrows); E: Duplex ultrasonography examination revealed an intimal flap and significant narrowing of the lumen secondary to the equal-echoic mural hematoma (ellipse); F: Carotid artery digital subtraction angiography showed tapering occlusion of the left ICA just distal to the carotid bifurcation (Rat tail sign) (arrow). ACA: Anterior cerebral artery; CCA: Common carotid artery; ECA: External carotid artery; MCA: Middle cerebral artery.
- Citation: Wang GM, Xue H, Guo ZJ, Yu JL. Cerebral infarct secondary to traumatic internal carotid artery dissection. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(20): 4773-4784
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i20/4773.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.4773