Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 26, 2020; 8(18): 4100-4108
Published online Sep 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i18.4100
Published online Sep 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i18.4100
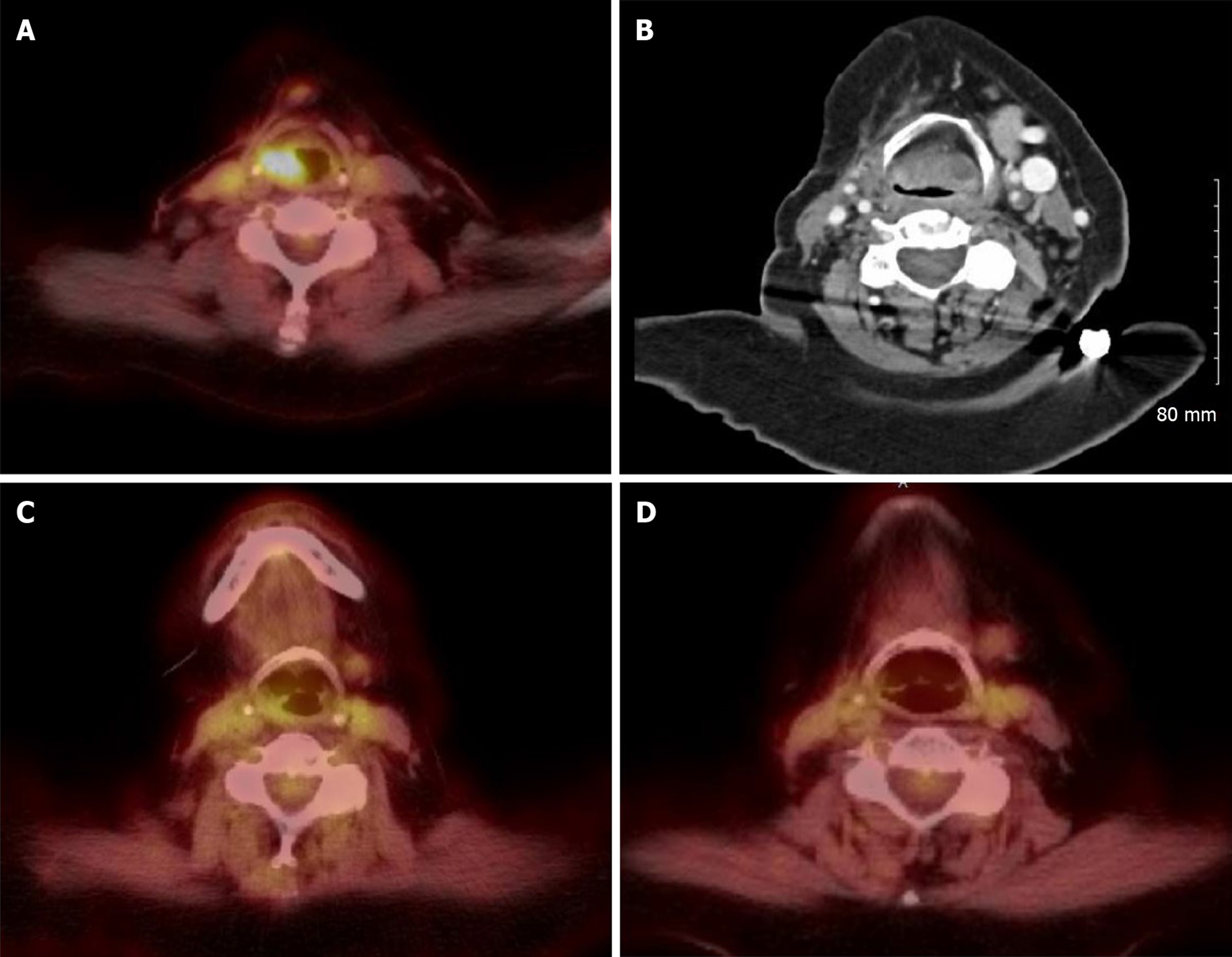
Figure 1 Positron emission tomography/computed tomography fusion images with fluorodeoxyglucose-18 and computed tomography soft tissue of neck.
A: New fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) avidity and soft tissue fullness in the right supraglottic fold extending to the epiglottis with mild leftward deviation of the trachea with narrowing in September 2018; B: Computed tomography neck soft tissue: considerable supraglottic soft tissue thickening, manifested most in posterior supraglottic larynx which threatens laryngeal airway in January 2019; C: Resolving right supraglottic soft tissue fullness and FDG activity 4 d after first dose of infliximab in March 2019; D: Improvement of right supraglottic soft tissue fullness and FDG activity in June 2019.
- Citation: Dang H, Sun J, Wang G, Renner G, Layfield L, Hilli J. Management of pembrolizumab-induced steroid refractory mucositis with infliximab: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(18): 4100-4108
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i18/4100.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i18.4100