Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2020; 8(14): 3064-3073
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i14.3064
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i14.3064
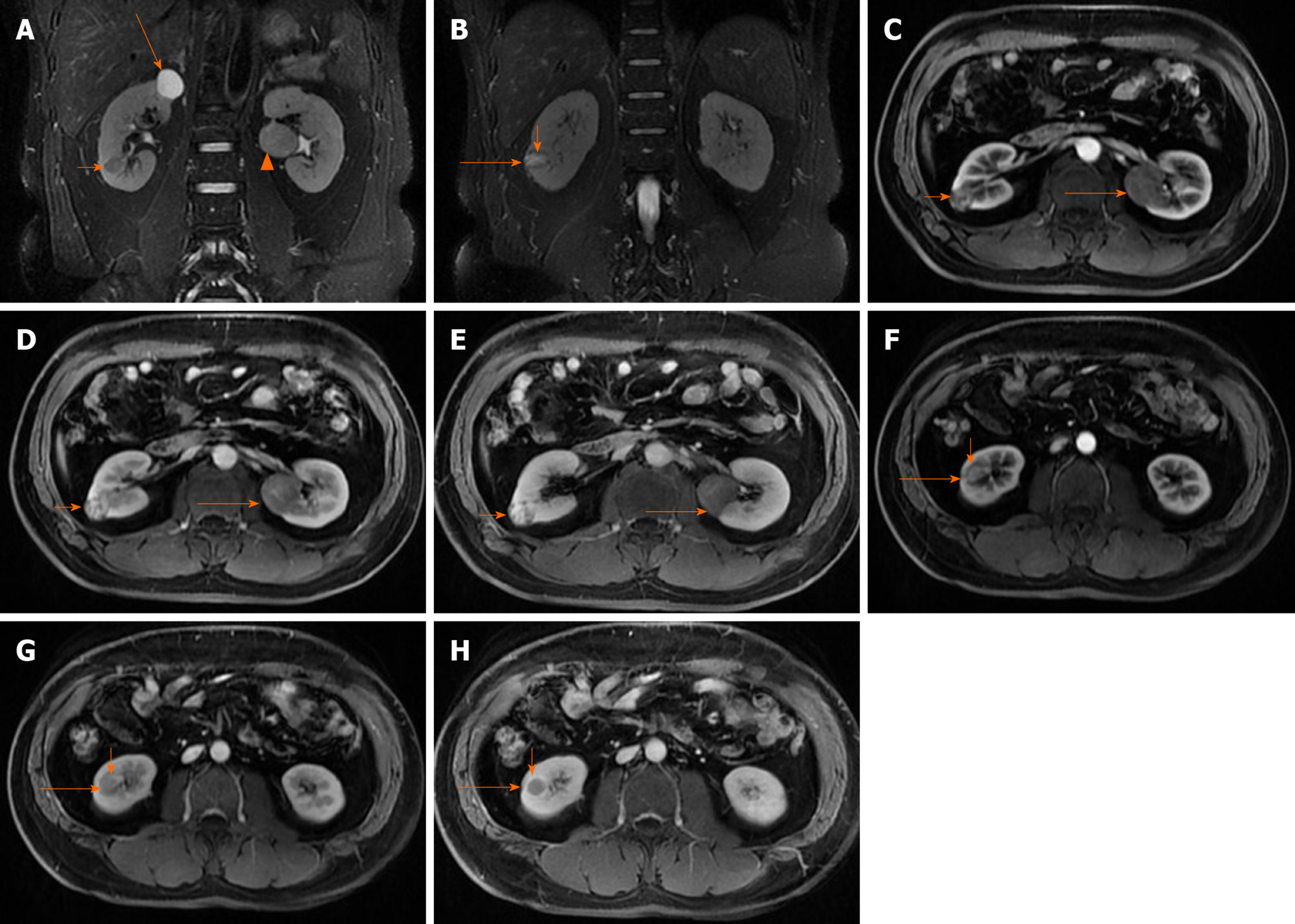
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging of the patient.
A: Pre-operative coronal fat-saturated series T2-weighted image of the patient demonstrating a cystic lesion at the upper pole of the right kidney showing strongly signal intensity (long arrow), and a homogeneous low signal intensity, solid mass at right kidney proven to be clear cell renal cell carcinoma (short arrow), and a solid mass, intermediate signal intensity in relation to the adjacent cortex, with a distinct hyposignal pseudocapsule at left kidney proven to be chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (CHRCC) (arrowhead); B: A heterogeneous hypersignal intensity (long arrow) with local cystic, with a distinct hyposignal pseudocapsule (short arrow) on right kidney, proven to be an oncocytic variant of CHRCC; C-E: Axial Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance image shows heterogeneous signal intensity mass in the right kidney, heterogeneous delayed enhancement, multiple small cysts without enhancement, proven to be an oncocytic variant of CHRCC (short arrow), and a solid mass in the middle of the left kidney, tend to present with progressive uptake in the contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), diagnosed as CHRCC (long arrow); F-H: Axial contrast-enhanced MRI shows a solid mass in the right kidney (long arrow), tends to present “fast in and fast out” pattern in contrast-enhanced MRI, and pseudocapsule (short arrow) delayed enhancement, diagnosed as clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
- Citation: Yang F, Zhao ZC, Hu AJ, Sun PF, Zhang B, Yu MC, Wang J. Synchronous sporadic bilateral multiple chromophobe renal cell carcinoma accompanied by a clear cell carcinoma and a cyst: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(14): 3064-3073
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i14/3064.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i14.3064