Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 26, 2020; 8(12): 2448-2463
Published online Jun 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i12.2448
Published online Jun 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i12.2448
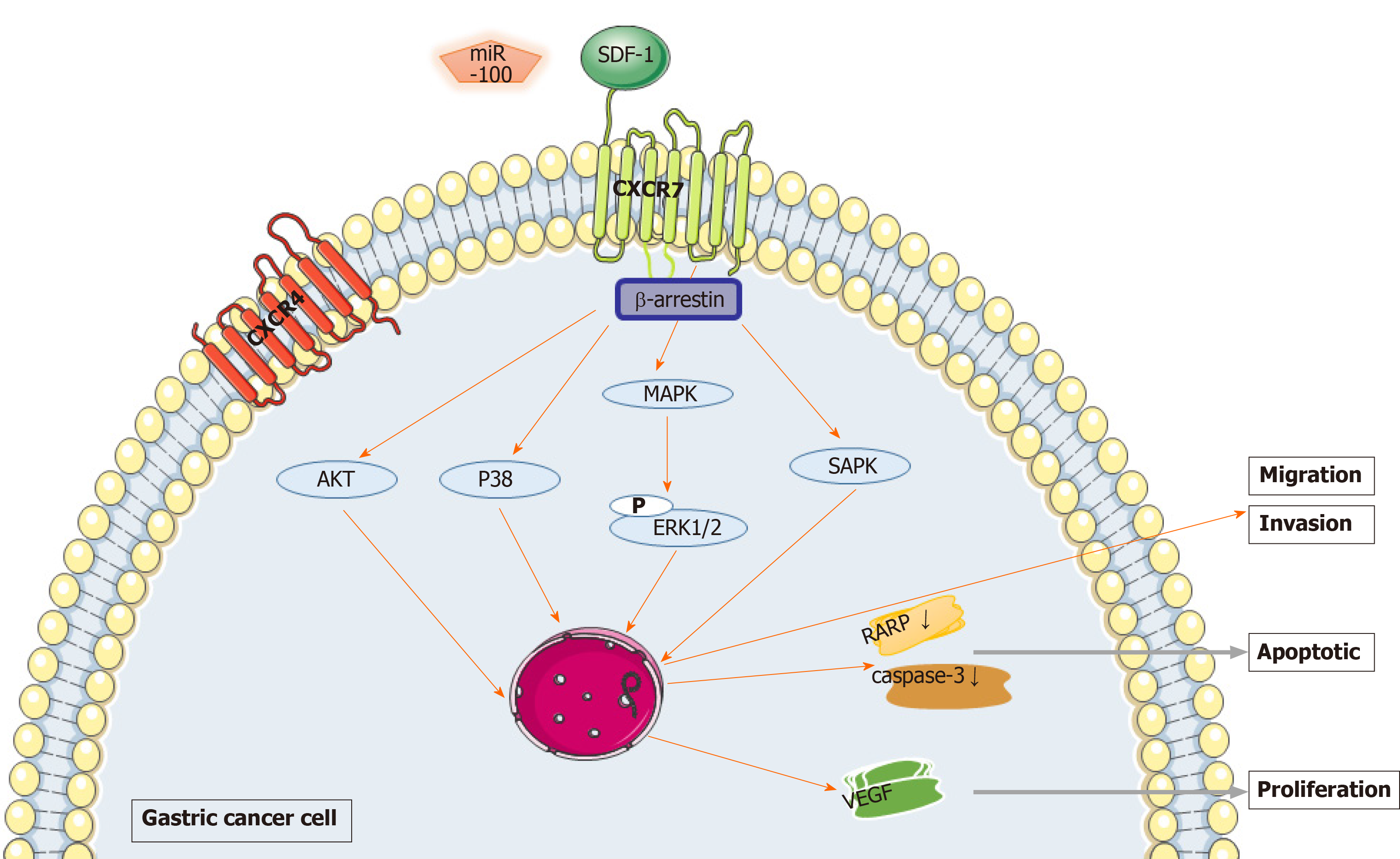
Figure 1 Mechanism of chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7 promoting the growth and metastasis of gastric cancer.
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7 (CXCR7) affects disease progression by stimulating proliferation, invasion, migration and adhesion of gastric cancer through β-arrestin dependent downstream signaling, including also known as Protein Kinase B, extracellular regulated protein kinases 1/2, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases, just another kinase 2/ serial advanced technology attachment 3/ cellular-myelocytomatosis, and stress-activated protein kinase pathways by combining with the stromal cell-derived factor-1. CXCR7 inhibits the processing of poly ADP-ribose polymerase and caspase-3 and induces an anti-apoptotic effect. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 promotes the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor in gastric cancer cells by binding CXCR7, thus causing angiogenesis in gastric cancer. CXCR7: Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7; Akt: Also known as Protein Kinase B, PKB; ERK1/2: Extracellular regulated protein kinases 1/2; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinases; JAK2: Just another kinase 2; STAT3: Serial advanced technology attachment 3; c-Myc: Cellular-myelocytomatosis; SAPK: Stress-activated protein kinase; SDF-1: Stromal cell-derived factor-1; PARP: Poly ADP-ribose polymerase; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Xin Q, Sun Q, Zhang CS, Zhang Q, Li CJ. Functions and mechanisms of chemokine receptor 7 in tumors of the digestive system. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(12): 2448-2463
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i12/2448.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i12.2448