Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 26, 2019; 7(6): 717-726
Published online Mar 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i6.717
Published online Mar 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i6.717
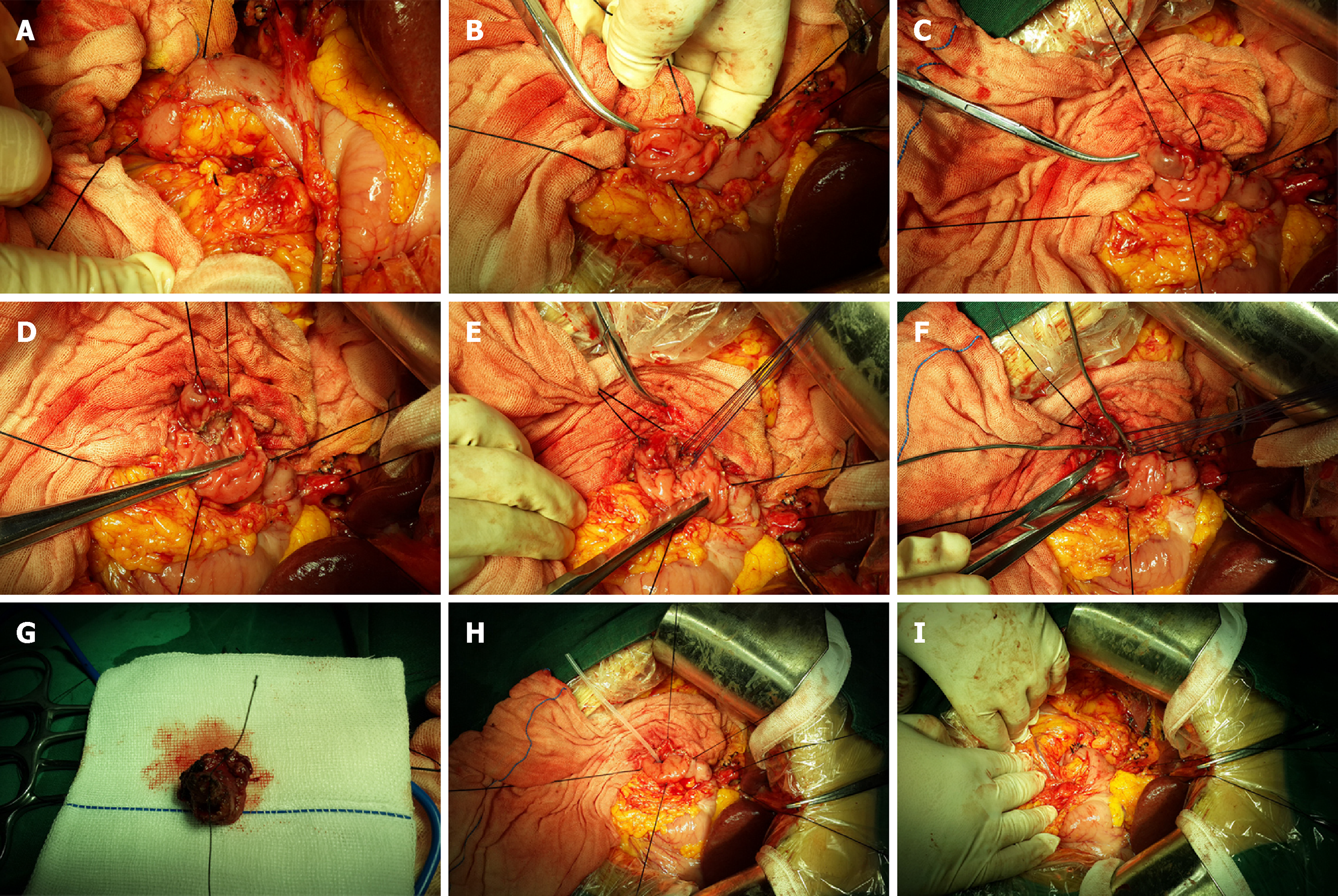
Figure 4 Surgical procedure.
A: Kocher incision, dissociation of the lateral peritoneum of the duodenal descending portion, exposure of the duodenal descending portion, and search for the position of the duodenal papilla; lesions were accurately detected; B: Anterior wall of the duodenum; lengthwise incision at the duodenal descending section showing the periampullary lesions; C: Exposure and lifting of the duodenal papilla using a transfixion suture; D: Maintaining an appropriate distance around the base of the periampullary tumor, we cut open the duodenal mucosa and the mucosal muscularis; E: The common bile duct and the main pancreatic duct end were anastomosed with the duodenal wall using interrupted sutures; F: The bile duct and the pancreatic duct passed through the biliary probes after replantation; G: Complete resection of the periampullary tumor; H: The supporting tube was inserted into the main pancreatic duct and fixed; I: The duodenal intestinal wall was closed with single-layer longitudinal suturing using absorbable sutures.
- Citation: Liu F, Cheng JL, Cui J, Xu ZZ, Fu Z, Liu J, Tian H. Surgical method choice and coincidence rate of pathological diagnoses in transduodenal ampullectomy: A retrospective case series study and review of the literature. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(6): 717-726
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i6/717.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i6.717