Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2019; 7(4): 452-465
Published online Feb 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i4.452
Published online Feb 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i4.452
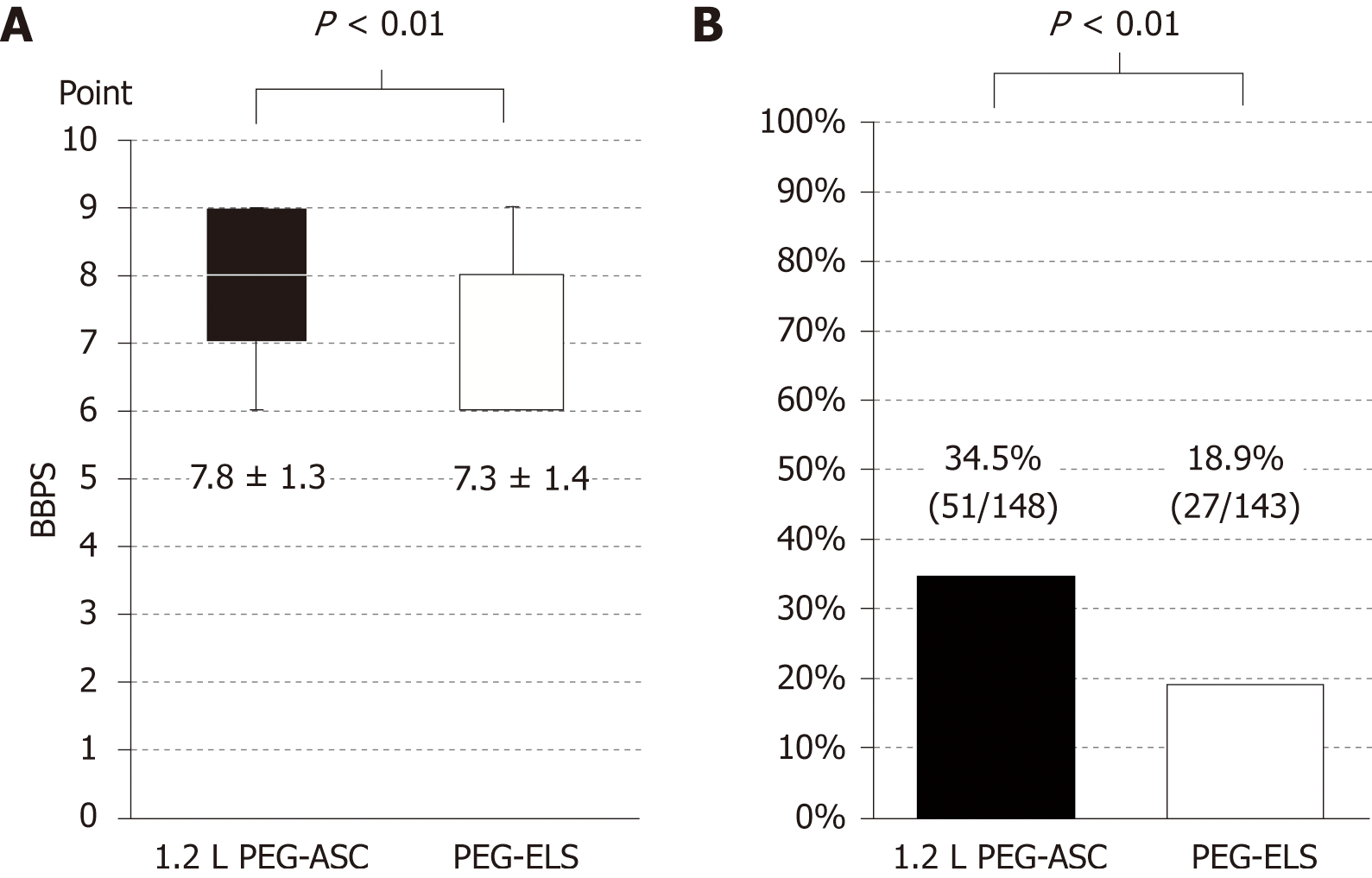
Figure 4 Difference in the cleansing quality and the frequency of cleansing operations to remove foam or bubbles between the 1.
2 L polyethylene glycol plus ascorbic acid group and the polyethylene glycol-based electrolyte solution group. A: Cleansing quality evaluated by the BBPS. The sum of each segmental score of BBPS was higher in the 1.2 L PEG-ASC group than in the PEG-ELS group (7.80 ± 1.37 vs 7.30 ± 1.40, P < 0.01 in ITT population, 7.76 ± 1.35 vs 7.29 ± 1.37, P < 0.01 in the per-protocol population). B: Frequency of cleansing operations to remove foam or bubbles. Foam or bubbles were observed more frequently in the 1.2 L PEG-ASC group than in the PEG-ELS group (35.7% vs 19.7%, P < 0.01). BBPS, Boston Bowel Preparation Scale; PEG-ASC, polyethylene glycol plus ascorbic acid; PEG-ELS, polyethylene glycol-based electrolyte solution.
- Citation: Tamaki H, Noda T, Morita M, Omura A, Kubo A, Ogawa C, Matsunaka T, Shibatoge M. Efficacy of 1.2 L polyethylene glycol plus ascorbic acid for bowel preparations. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(4): 452-465
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i4/452.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i4.452