Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 26, 2019; 7(24): 4172-4185
Published online Dec 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i24.4172
Published online Dec 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i24.4172
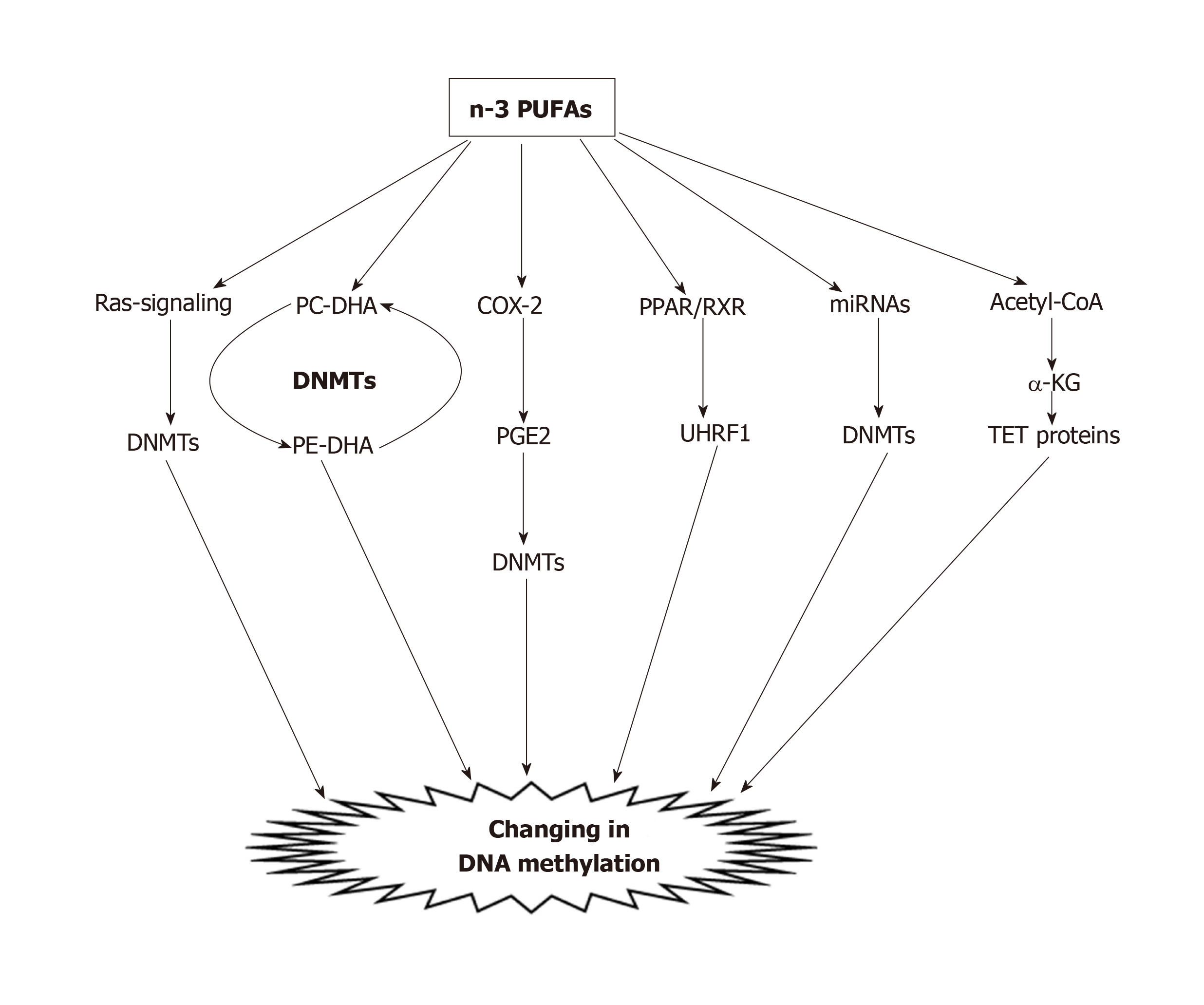
Figure 2 A model of the possible mechanisms by which polyunsaturated fatty acids can alter DNA methylation in colorectal cancer.
DNMTs: DNA methyltransferases; DHA: Docosahexaenoic acid; PE-DHA: Phosphatidylethanolamine-DHA; PC-DHA: Phosphatidylcholine-DHA; PUFA: Poly unsaturated fatty acid; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; PPARs: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors; RXR: Retinoid X receptor; UHRF1: Ubiquitin-like protein containing PHD and RING finger domains 1; miRNAs: MicroRNAs; α-KG: α-ketoglutarate; TET: Ten-eleven translocation.
- Citation: Moradi Sarabi M, Mohammadrezaei Khorramabadi R, Zare Z, Eftekhar E. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and DNA methylation in colorectal cancer. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(24): 4172-4185
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i24/4172.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i24.4172