Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2019; 7(23): 4029-4035
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4029
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4029
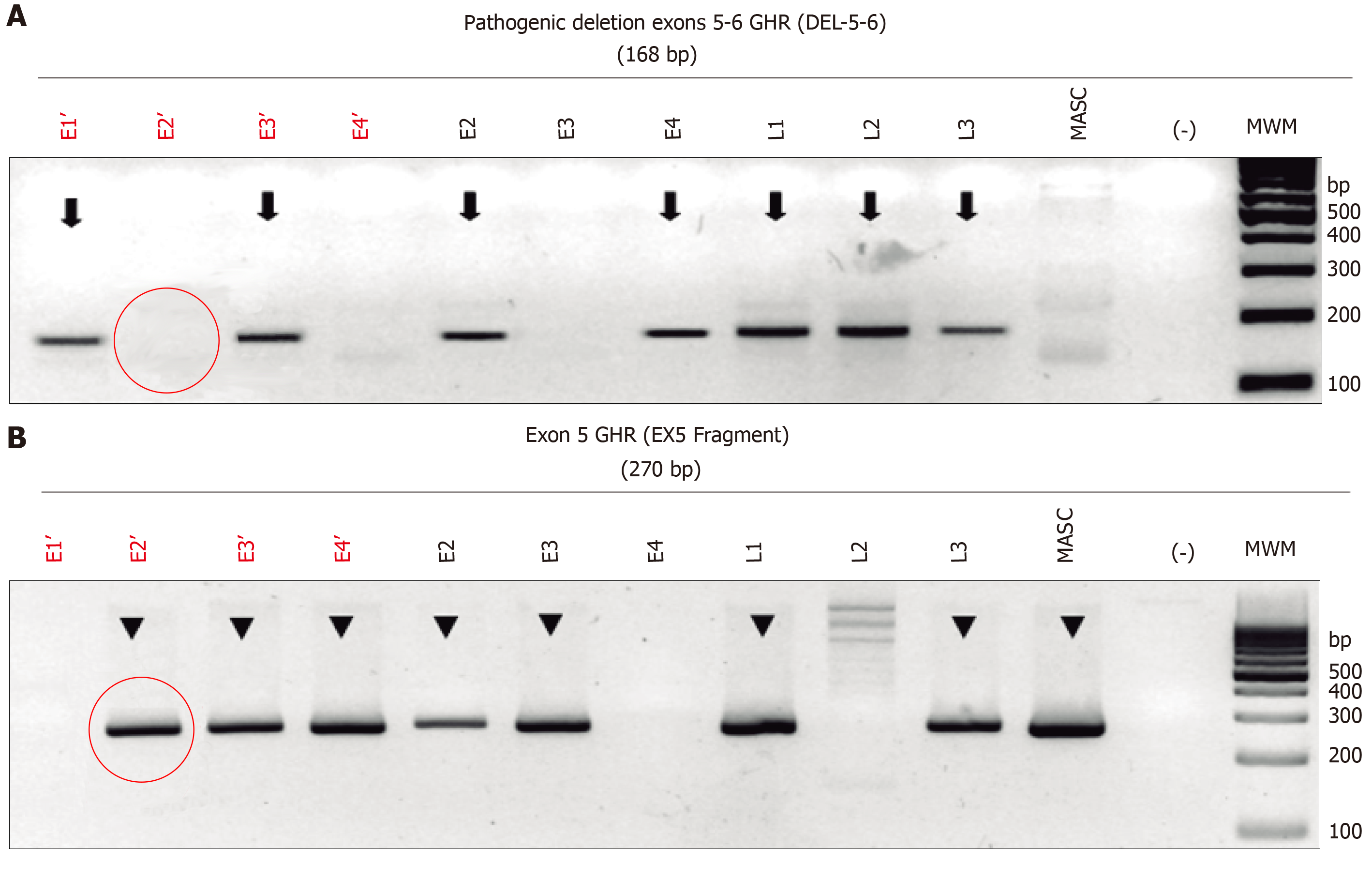
Figure 1 Electrophoresis of the monoplex polymerase chain reaction assay to identify the deletion of exons 5 and 6 (del5-6) of the growth hormone receptor gene for in vitro fertilization embryos.
Lanes E1 to E4 show the whole genome amplification-DNA corresponding to the embryos being analyzed. Lanes L1 to L3 shown the controls previous known to have the deletions. L1 (paternal: heterozygous for del5-6), L2 (affected child: homozygous for del5-6), L3 (maternal: heterozygous for del5-6), masculine (positive control for a homozygous male normal), (-) water control, MWM molecular weight marker (right lane). E1 and E3 show a del5-6, only E1 shows a deletion of ex5, meaning that E1 is homozygous affected, E3 is a heterozygous carrier, and E2 and E4 are wild-types for the deletion causing Laron syndrome. GHR: Growth hormone receptor.
- Citation: Neumann A, Alcántara-Ortigoza MÁ, González-del Ángel A, Camargo-Diaz F, López-Bayghen E. Diagnosis of Laron syndrome using monoplex-polymerase chain reaction technology with a whole-genome amplification template: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(23): 4029-4035
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i23/4029.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4029