Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2019; 7(22): 3683-3697
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3683
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3683
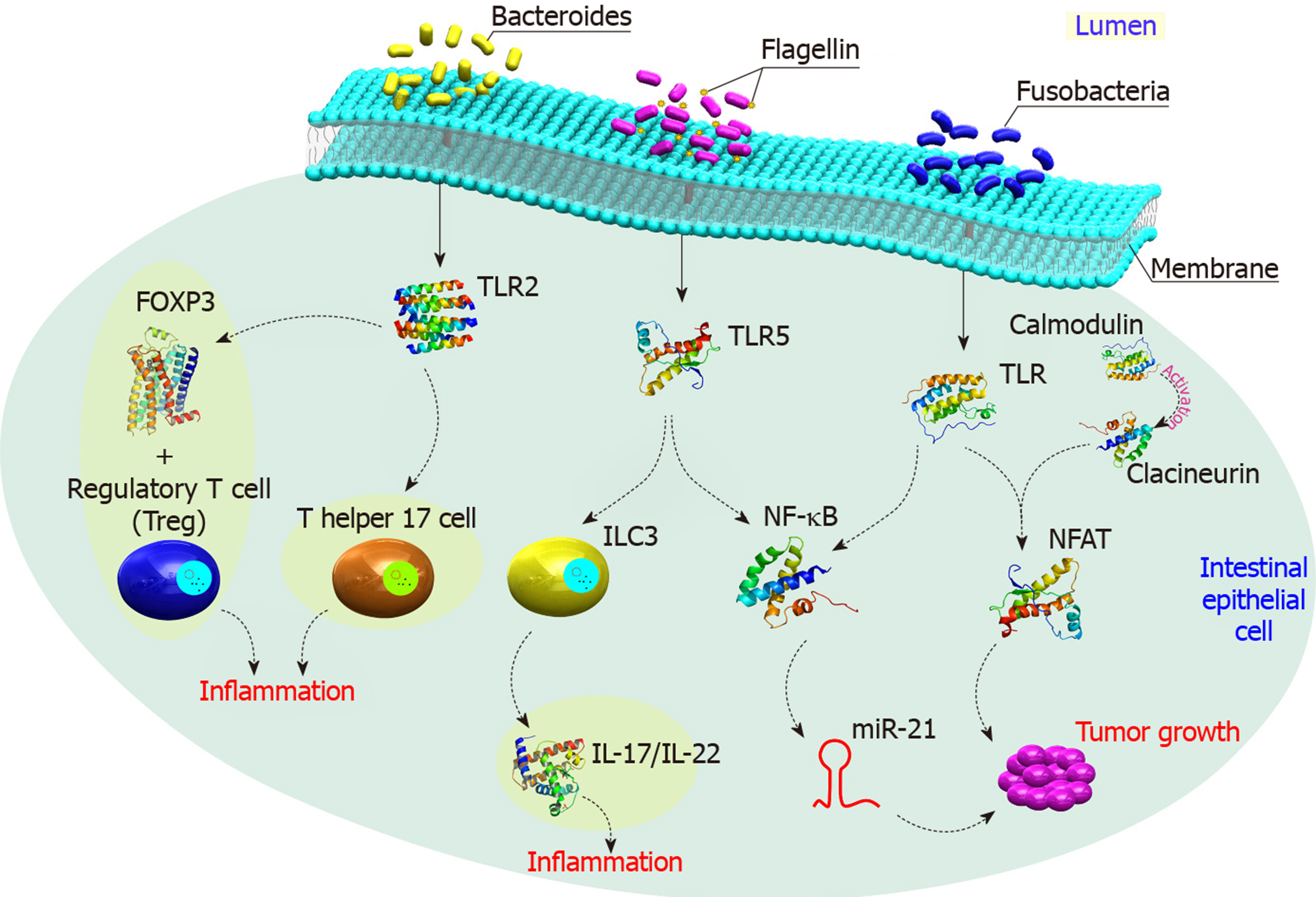
Figure 4 Different gut microbiota generate different oncometabolites.
Bacteroides expresses specific signaling substances to activate toll-like receptor 2 (TLR 2), which functions in two different ways; activation of FOX3 to trigger Treg activation leading to inflammation. The other way is the activation of T helper 17 cells that also triggers inflammation. Flagellin, a product of flagellated bacteria, activates also TLR 5 to activate innate lymphoid cells 3 and then IL 17 and 22 that initiate inflammation. TLR 5 also works on nuclear factor κB to activate miR-21 that has a role in initiating cancer carcinogenesis (CRC). Meanwhile, Fusobacteria can stimulate a specific type of TLR that activates nuclear factor of activated T cell via calmodulin-based calcineurin to initiate CRC. CRC: Colorectal cancer; IL: Interleukin; ILC: lymphoid cells; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; NFAT: Nuclear factor of activated T cell; TLR: Toll-like receptor; Treg: T regulatory cell.
- Citation: Sabit H, Cevik E, Tombuloglu H. Colorectal cancer: The epigenetic role of microbiome. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(22): 3683-3697
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i22/3683.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3683