Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2019; 7(20): 3226-3236
Published online Oct 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i20.3226
Published online Oct 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i20.3226
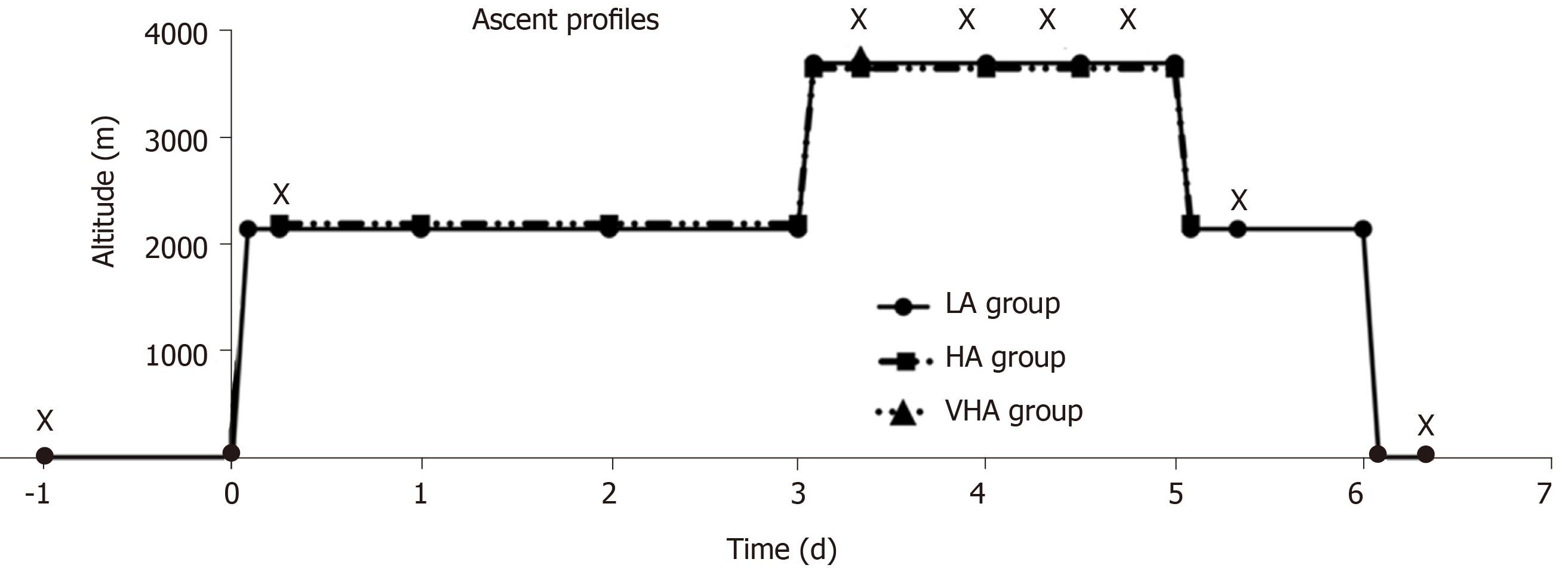
Figure 1 Altitude profiles of three groups and examination time points.
The low altitude (LA) group flew to 2261 m above sea level (ASL). Three days later, they flew with the high altitude (HA) group to 3750 m ASL where both groups stayed for 2 d. The LA group flew back to 2261 m ASL and stayed for 1 d before returning to 44 m. Intraocular pressure, vital values and hematological values were measured before and during exposure to 2261 m and 3750 m ASL in LA, HA, and very high altitude groups. X: Examination time points; LA: Low altitude; HA: High altitude; VHA: Very high altitude.
- Citation: Xie Y, Sun YX, Han Y, Yang DY, Yang YQ, Cao K, Li SN, Li X, Lu XX, Wu SZ, Wang NL. Longitudinal observation of intraocular pressure variations with acute altitude changes. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(20): 3226-3236
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i20/3226.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i20.3226