Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 26, 2019; 7(2): 191-202
Published online Jan 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i2.191
Published online Jan 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i2.191
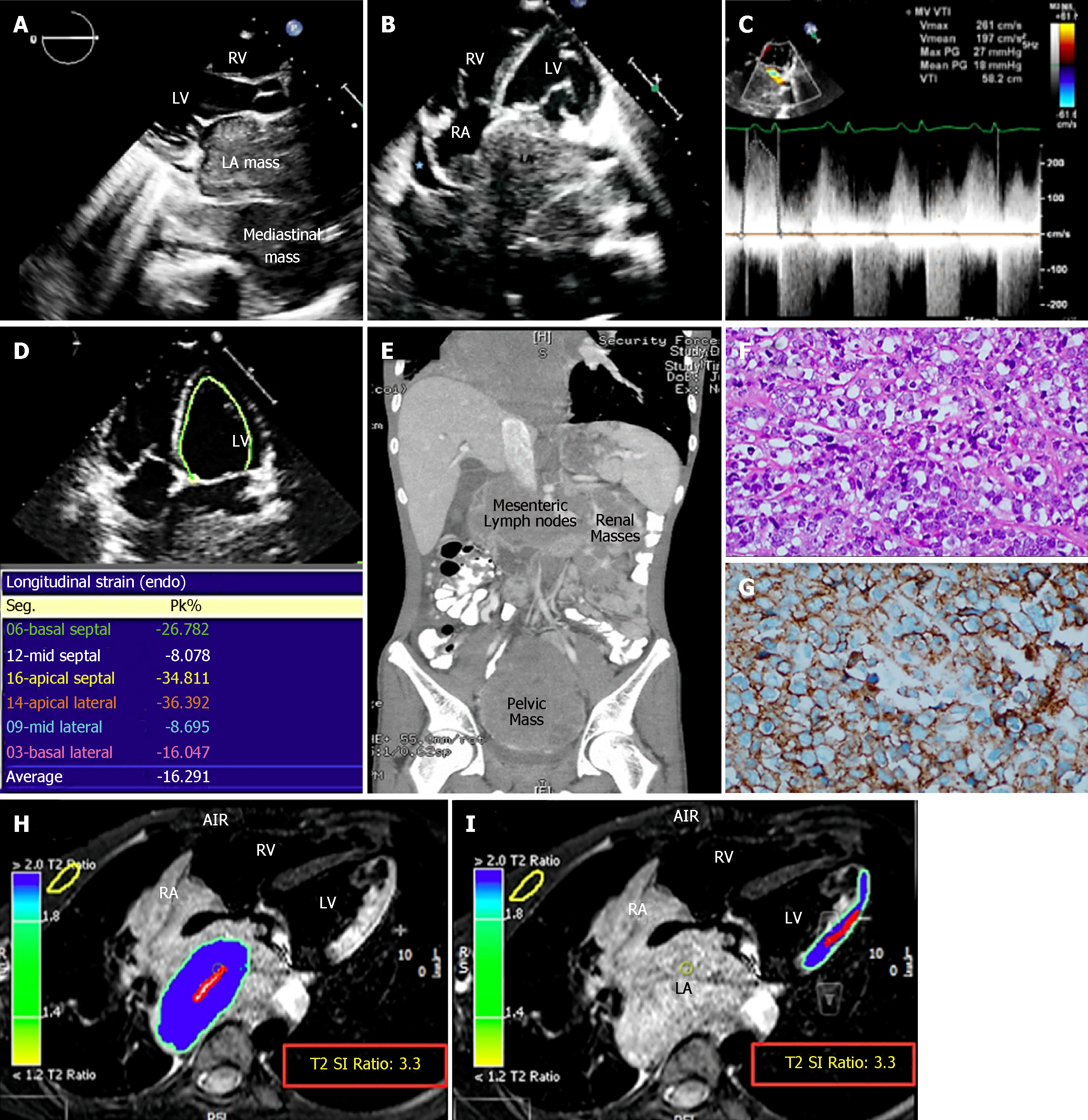
Figure 1 The patient’s initial imaging and histopathological findings.
A and B: Echocardiographic findings: (A) Parasternal long axis and (B) apical 4-chamber views demonstrating a very large LA mass extending from the mediastinum and involving the RA. Minimal pericardial effusion is noted (blue star); C: Continuous-wave Doppler showing functional mitral stenosis and regurgitation; D: Strain imaging of the LV in a 4-chamber view showing impaired lateral wall strain due to lymphoma infiltration; E: Contrast-enhanced thoracoabdominal computed tomography (CT) scan in a coronal view showing mesenteric, renal, and pelvic masses; F: Histopathology of the pelvic mass revealed atypical large lymphoid cells with prominent nucleoli and abundant cytoplasm; G: Immunohistochemistry was strongly positive for CD20; H and I: First CMRI images, STIR, axial views showing high signal intensity of the LA mass (H), and lateral LV wall (I), indicating high fluid content. The T2 signal intensity (SI) ratio of the LA mass and lateral LV wall are identical, indicating infiltration of the lateral LV wall by the mediastinal lymphoma. LA: Left atrium; RA: Right atrium; RV: Right ventricle; LV: Left ventricle; CMRI: Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; STIR: T2-weighted short-tau inversion recovery images; SI: Signal intensity.
- Citation: Al-Mehisen R, Al-Mohaissen M, Yousef H. Cardiac involvement in disseminated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, successful management with chemotherapy dose reduction guided by cardiac imaging: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(2): 191-202
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i2/191.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i2.191