Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2018; 6(15): 961-984
Published online Dec 6, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i15.961
Published online Dec 6, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i15.961
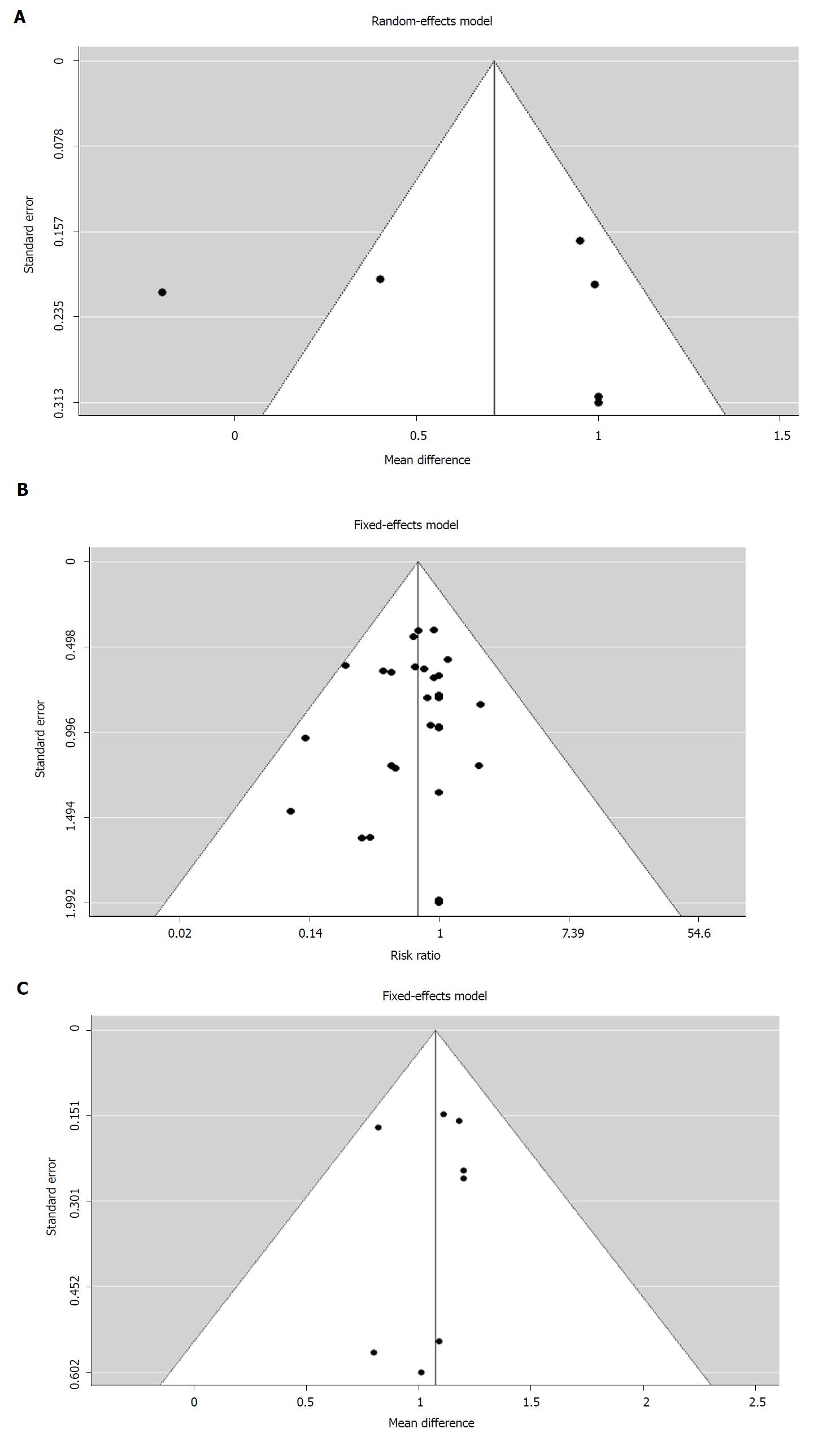
Figure 10 Funnel plots showing the relationship between the relative risk and its standard error for (A) 7 studies used in a random effects meta-analysis evaluating the efficacy of Medilac-S® in combination with conventional drug therapy on change in mean endoscopic score (B) 8 studies used in a fixed effects meta-analysis evaluating the efficacy of Medilac-S® in combination with conventional drug therapy on change in mean endoscopic score and (C) 30 studies used in a fixed effects meta-analysis evaluating the efficacy of Medilac-S® in combination with conventional drug therapy on change in the number of reported adverse events.
- Citation: Sohail G, Xu X, Christman MC, Tompkins TA. Probiotic Medilac-S® for the induction of clinical remission in a Chinese population with ulcerative colitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(15): 961-984
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i15/961.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i15.961