Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2018; 6(15): 961-984
Published online Dec 6, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i15.961
Published online Dec 6, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i15.961
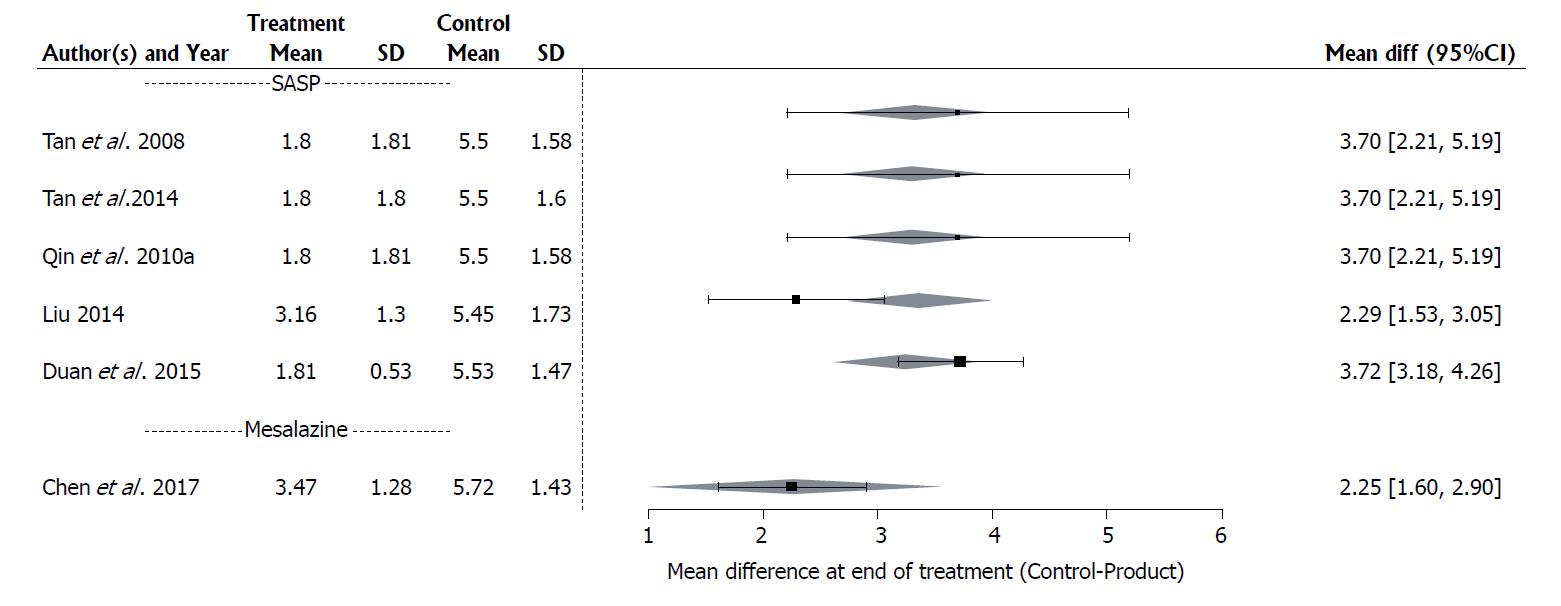
Figure 5 Forest plot of the results of a mixed effects meta-analysis with a moderator for concomitant drug therapy, with 6 studies evaluating the effect of Medilac-S® in combination with conventional drug therapy on the change in mean Sutherland index score evaluating three clinical symptoms and a global physician’s assessment.
“Mean” is the mean index and “SD” is the standard deviation for each study; the difference between the treatment and control of the mean indices at the end of the study and its 95%CI is listed on the right hand side of the graph; the 95%CI for the estimated mean difference for each concomitant drug therapy category is shown as a shaded diamond with the endpoints of the diamond being the CI endpoints and the location of the maximum width of the diamond being at the estimated mean difference for that drug type.
- Citation: Sohail G, Xu X, Christman MC, Tompkins TA. Probiotic Medilac-S® for the induction of clinical remission in a Chinese population with ulcerative colitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(15): 961-984
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i15/961.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i15.961