Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2018; 6(14): 745-752
Published online Nov 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.745
Published online Nov 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.745
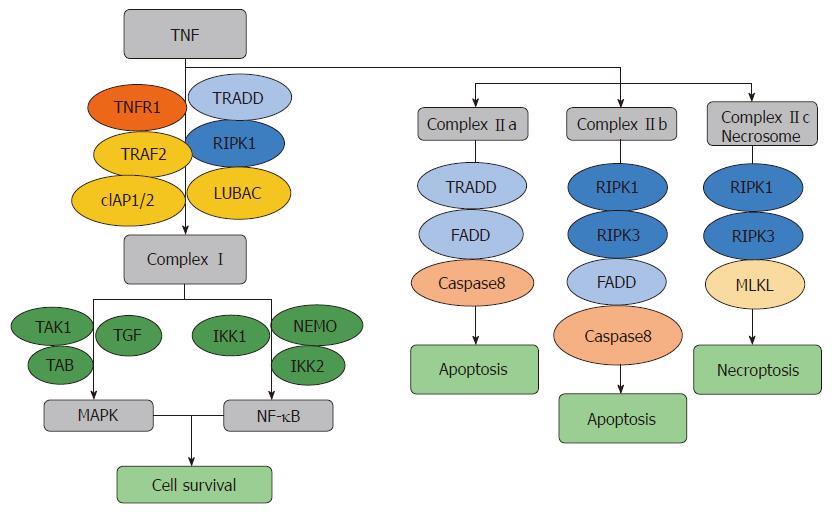
Figure 1 Tumor necrosis factor-α pathway for necroptosis.
Combination of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and TNF-R1 can raise TNF-α receptor associated death domain protein (TRADD), receptor interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1), TNFR-associated factor 2, cellular inhibitors of apoptosis (cIAP1 or cIAP2) and linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex to form Complex I, which can activate the Mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-κB pathways by binding the TGF–TAK1–TAB and IKK1–IKK2–NEMO complexes, leading to cell survival. Complex IIa [consists of TRADD, Fas-associated death domain (FADD) and caspase-8] forms when Complex I is unstable and mediates apoptosis independent of RIPK1. Complex IIb (consists of RIPK1, RIPK3, FADD and caspase-8) forms when cIAP inhibitors are present or IAPs are knocked out, TAK1 inhibitors are present or TAK1 is knocked out, and NEMO is knocked out, and mediates apoptosis dependent on the binding of RIPK1 and RIPK3. Complex IIc (consists of RIPK1, RIPK3 and MLKL) forms when caspase-8 is inhibited or missing and leads to necroptosis. TRAF2: TNFR-associated factor 2; cIAP1 or cIAP2: Cellular inhibitors of apoptosis; LUBAC: Linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex; TRADD: TNF-α receptor associated death domain protein; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; FADD: Fas-associated death domain.
- Citation: Li S, Ning LG, Lou XH, Xu GQ. Necroptosis in inflammatory bowel disease and other intestinal diseases. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(14): 745-752
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i14/745.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.745