Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2018; 6(13): 577-588
Published online Nov 6, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i13.577
Published online Nov 6, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i13.577
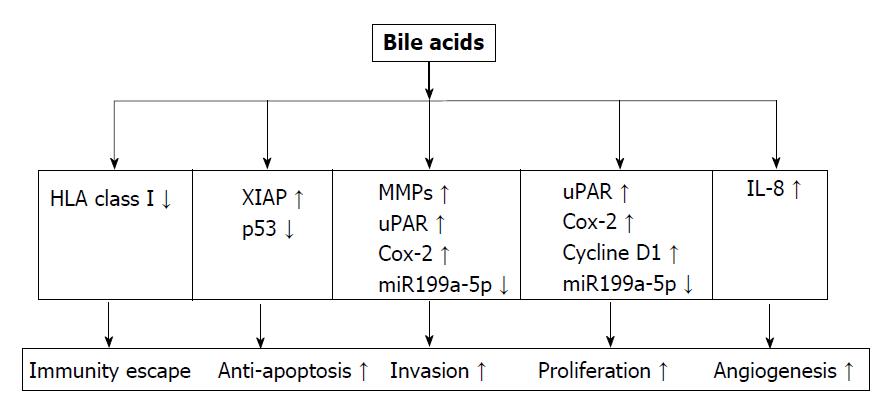
Figure 4 Bile acids regulate gene expression towards tumor development.
Bile acids (BAs) decrease the expression of human leukocyte antigen class I antigens on the surface of colorectal cancer cells, helping cancer cells escape from immune surveillance. They enhance the apoptosis resistance ability of cancer cells via up-regulating XIAP expression, and degrading p53 protein. BAs stimulates cancer proliferation and invasion via their effect on a series of oncogenes including MMPs, uPAR, Cox-2, Cycline D1, and miR199a-5p. By inducing IL-8 expression, BAs enhance angiogenesis activity for tumor growth and metastasis. HLA: Human leukocyte antigen; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; UPAR: Urokinase receptor; Cox: Cyclooxygenase; IL-8: Interleukin-8; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor, XIAP: X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein.
- Citation: Nguyen TT, Ung TT, Kim NH, Jung YD. Role of bile acids in colon carcinogenesis. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(13): 577-588
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i13/577.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i13.577