Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 26, 2018; 6(10): 335-343
Published online Sep 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i10.335
Published online Sep 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i10.335
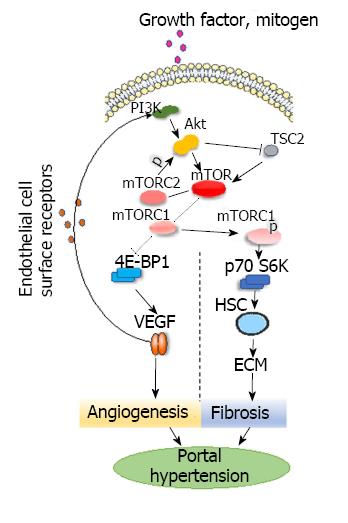
Figure 1 PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathways in the development of hepatic portal hypertension.
PI3K-AKT-mTOR: In vivo, growth factors, mitogens and hormones interact with PI3K, which activates Akt that then activates mTOR. Mammals have two mTOR complexes: mTORC1 and mTORC2. Akt can phosphorylate mTORC1 and then activate p70S6K via phosphorylation to inhibit 4E-BP1. Activated p70S6K promotes the proliferation of HSCs and stimulates both the production of ribosomes and the synthesis of collagen and other extracellular matrix constituents. mTORC1 can inhibit 4E-BP1, promote the splitting of VEGF, and regulate angiogenesis. Akt can inactivate tuberous sclerosis complex 2 and enhance mTOR activity. mTORC2 regulates Akt. Akt: Protein kinase B; ECM: Extracellular matrix; HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; mTOR: Mammalian targets of rapamycin; mTORC: Mammalian targets of rapamycin complex; p70S6K: p70 ribosomal protein S6 Kinase; TSC2: Tuberous sclerosis complex 2; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; 4E-BP1: 4E-binding protein-1.
- Citation: Xu W, Liu P, Mu YP. Research progress on signaling pathways in cirrhotic portal hypertension. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(10): 335-343
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i10/335.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i10.335